Boost Your Child’s Visual Perception Skills at Home
Last Updated: June 3, 2024
Have you noticed your child struggling to complete puzzles, mix up letters like “b” and “d,” or find objects in a cluttered room? These challenges may hint at difficulties with visual perception. Visual perception skills, simply put, is the brain’s ability to interpret what the eyes see. It’s not just about having perfect vision but understanding and making sense of the world.
This skill is crucial for kids in everyday tasks like reading, writing, solving puzzles, dressing, and even locating their favorite sock under the bed. Without good visual perceptual abilities, children can struggle academically and socially, impacting their confidence and self-esteem.
Read More: Help Your Child Thrive: Boost Visual Perception Skill
What is Visual Perception?
Visual perception is the brain’s ability to understand and understand what the eyes see. It’s not the same as visual acuity, which measures how a person can see (for example, 20/20 vision). Your child can have 20/20 vision and still struggle with visual perceptual processing.
How Does Visual Perception Work?
Think of visual perception as a team effort between the eyes and the brain. The eyes capture information from the environment and send it to the brain, which interprets these signals to recognize shapes, patterns, colors, and spatial relationships.
Here’s a simple way to understand it:
- Eyes See: The eyes detect light, colors, shapes, and movement.
- Brain Interprets: The brain processes the signals to identify objects, understand spatial relationships, and recognize patterns.
- Makes Sense: The brain gives meaning to what is seen, allowing your child to read, write, play, and navigate their world effectively.
Without effective visual perception skills, children may struggle with tasks like finding a hidden toy in a cluttered room, differentiating letters, or completing puzzles.
Read More: Shapes Around Us: Interactive Learning at Home for Children
The Importance of Visual Perception in Childhood Development
Visual perception is crucial in children’s everyday lives, influencing their academic performance, play activities, and confidence. Let’s delve into why developing these skills is so important:
1. Academic Success:
- Reading and Writing: Kids with strong visual perception can easily identify letters and words, leading to smoother reading and writing experiences.
- Math Skills: Understanding shapes, patterns, and spatial relationships helps with counting, problem-solving, and geometry.
- Copying from the Board: Recognizing and remembering sequences of words or numbers enables kids to copy information from the board or a book without getting confused.
2. Play and Recreational Activities:
- Puzzles and Games: Recognizing shapes and patterns is essential for completing puzzles, playing board games, and engaging in scavenger hunts.
- Sports Coordination: Visual spatial skills help kids judge distances and understand their position in relation to other objects, improving sports coordination.
- Drawing and Crafting: Differentiating colors and shapes enables children to draw, color, and craft with precision.
3. Independence and Confidence:
- Self-Care Tasks: Finding clothes in a messy room, tying shoelaces, or sorting toys are all easier with strong visual perception skills.
- Organizational Skills: Kids can better organize their belongings, leading to tidier rooms and school desks.
- Confidence Boost: Successfully completing tasks like reading, writing, and playing games builds confidence and self-esteem.
4. Social Interaction:
- Recognizing Social Cues: Visual perception helps children identify facial expressions and body language, which is essential for effective social interaction.
- Participating in Group Activities: Better visual discrimination skills mean kids can follow group games, sports, and classroom activities with ease.
Common Signs of Visual Perception Difficulties
Have you noticed your child facing challenges like trouble solving puzzles, mixing up letters, or losing their place while reading? These are just a few signs that may indicate difficulties with visual perception. Here are some common challenges to look out for:
1. Trouble with Puzzles and Dot-to-Dots:
- Difficulty completing puzzles, whether they’re simple 2-piece ones or more complex jigsaws.
- Struggling with dot-to-dot worksheets and mazes.
2. Differentiating Letters and Numbers:
- Confusing similar-looking letters like “b” and “d” or “p” and “q.”
- Reversing numbers when writing (e.g., writing “3” backward).
3. Losing Place While Reading or Writing:
- Skipping lines or losing place while reading text or copying information from the board.
- Struggling to focus on individual words or letters on a cluttered page.
4. Difficulty Following Sequences:
- Struggling to recall the order of letters in words or numbers in math problems.
- Forgetting where to start reading or writing on the page.
5. Issues with Spatial Concepts:
- Confusion with directions like “up,” “down,” “in,” “out,” or “next to.”
- Difficulty understanding spatial relationships between objects.
6. Visual Attention and Discrimination Problems:
- Unable to filter out visual distractions, like movement or colorful bulletin boards.
- Trouble finding specific items in a busy environment, like a cluttered desk.
7. Struggles with Self-Care Tasks:
- Finding it hard to dress independently or match shoes and socks.
- Difficulty organizing personal belongings.
8. Avoidance and Frustration:
- Avoiding activities that require visual perceptual skills, like drawing or writing.
- Becoming easily frustrated with precise tasks involving eye-hand coordination.
9. Poor Academic Performance:
- Falling behind in reading, writing, math, and other academic tasks due to visual perception challenges.
If you recognize these signs in your child, don’t worry! The good news is that targeted activities and support can improve visual perception skills.
Core Visual Perceptual Skills
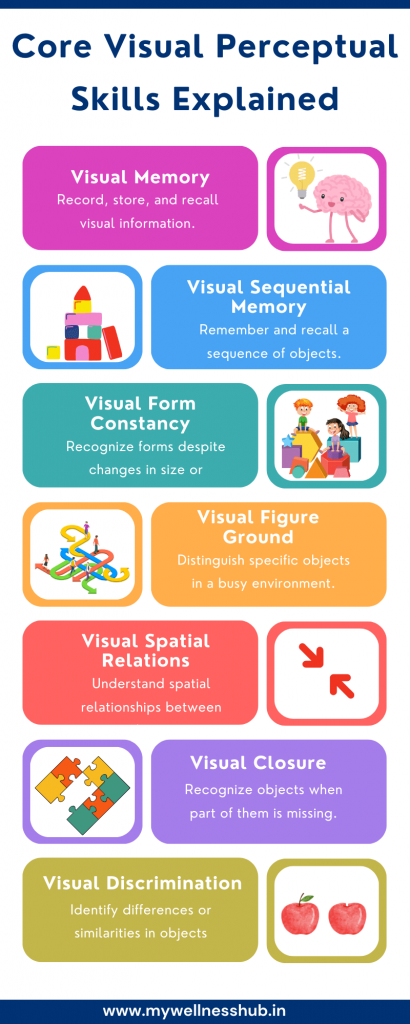
Visual perception skills are essential for children to make sense of the visual world around them. Let’s look at some of the key skills and how they impact everyday activities:
1. Visual Memory
- Definition: The ability to record, store, and recall visual information.
- Example: Remembering the shapes of letters or how to draw them correctly after seeing them once.
- Everyday Impact: Helps with reading, writing, and recognizing familiar objects like toys or clothes.
2. Visual Sequential Memory
- Definition: The ability to remember and recall a sequence of visual information.
- Example: Memorizing the order of numbers in a phone number or steps in a math equation.
- Everyday Impact: Essential for spelling words correctly, remembering math sequences, and following a series of instructions.
3. Visual Form Constancy
- Definition: Recognizing that a form or shape is the same, even if made smaller, larger, or reversed.
- Example: Differentiating between letters like “b” and “d” or “p” and “q.”
- Everyday Impact: Helps children recognize letters and words regardless of size, position, or orientation.
4. Visual Figure Ground
- Definition: The ability to distinguish specific objects from a busy background.
- Example: Finding a toy in a cluttered room or locating a specific word on a crowded page.
- Everyday Impact: Helps children focus on individual words while reading or find their favorite toy.
5. Visual Spatial Relations
- Definition: Understanding the spatial relationship between objects and oneself.
- Example: Judging how close an object is or placing a puzzle piece correctly.
- Everyday Impact: Vital for handwriting (spacing between words), sports (judging distance to catch a ball), and everyday tasks like dressing.
6. Visual Closure
- Definition: Recognizing an object when part of it is missing.
- Example: Identifying a partially drawn letter or completing a puzzle with missing pieces.
- Everyday Impact: Helps children read words with missing letters or identify familiar objects even when they are partly hidden.
7. Visual Discrimination
- Definition: The ability to identify differences or similarities between objects.
- Example: Spotting the difference between two pictures or distinguishing between similar-looking letters like “m” and “n.”
- Everyday Impact: Crucial for reading, writing, and recognizing differences between similar objects.
How to Enhance Visual Perception
Fun Activities at Home
As parents, you can help your child improve visual perception skills through fun, interactive games that can be done right at home. Here are some simple activities to get started:
1. Scavenger Hunts
- How to Play: Create a list of specific items for your child to find around the house or yard (e.g., something round, green, something you can wear).
- Skills Developed:
- Figure Ground: Finding specific objects in a busy environment.
- Visual Discrimination: Identifying differences or similarities between objects (e.g., different colors or shapes).
- Tips:
- Start with easy objects and gradually increase difficulty.
- Use themes like “things you wear” or “things that roll” to keep it interesting.
2. Dot-to-Dot or Maze Puzzles
- How to Play: Provide your child with worksheets or books that contain dot-to-dot puzzles or mazes.
- Skills Developed:
- Visual Closure: Recognizing a whole picture from incomplete lines or dots.
- Visual Sequential Memory: Following a specific sequence to connect the dots or navigate the maze.
- Tips:
- Choose puzzles appropriate to your child’s age and skill level.
- Encourage them to draw the complete picture after finishing the dot-to-dot.
3. Memory Games
- How to Play: Use matching cards (like Memory or Concentration games) and lay them face down. Take turns flipping two cards to find matching pairs.
- Skills Developed:
- Visual Memory: Remembering visual information and recalling it later.
- Visual Form Constancy: Recognizing that an object is the same despite different orientations or sizes.
- Tips:
- Start with fewer pairs for younger children and increase pairs as they improve.
- Use different themes like animals, numbers, or shapes.
4. Sorting Games
- How to Play: Gather various objects like buttons, toys, or blocks and ask your child to sort them by color, size, or shape.
- Skills Developed:
- Visual Discrimination: Differentiating objects based on their visual characteristics.
- Visual Form Constancy: Recognizing objects despite size or orientation changes.
- Tips:
- Mix different objects together and encourage sorting in multiple ways (by color, then by shape).
- Use everyday items like coins, clothes, or utensils for added variety.
Also read: Fun Sorting Games to Boost Your Child’s Thinking at Home
5. Picture Drawing
- How to Play: Draw or print partially completed pictures and ask your child to finish them.
- Skills Developed:
- Visual Closure: Recognizing and completing a whole picture.
- Visual Form Constancy: Understanding shapes and patterns even with missing parts.
- Tips:
- Start with simple shapes and gradually increase complexity.
- Encourage your child to imagine and draw the missing parts themselves.
Visual Perception Activities & Skills Chart
| Activity | Description | Skills Developed |
|---|---|---|
| Scavenger Hunts | Create a list of items for your child to find around the house or yard. | – Figure Ground: Finding objects in a busy environment. – Visual Discrimination: Identifying differences and similarities between objects |
| Dot-to-Dot Puzzles | Provide worksheets or books that contain dot-to-dot puzzles. | – Visual Closure: Recognizing whole pictures from incomplete lines. – Visual Sequential Memory: Following a specific sequence to connect dots |
| Memory Games | Use matching cards (like Memory or Concentration games) and lay them face down. Take turns flipping two cards to find matching pairs. | – Visual Memory: Remembering visual information and recalling it later. – Visual Form Constancy: Recognizing objects despite changes in orientation or size |
| Sorting Games | Gather objects like buttons or toys and ask your child to sort them by color, size, or shape. | – Visual Discrimination: Differentiating objects based on their visual characteristics. – Visual Form Constancy: Recognizing objects regardless of size or orientation changes |
| Picture Drawing | Draw or print partially completed pictures and ask your child to finish them. | – Visual Closure: Recognizing and completing a whole picture. – Visual Form Constancy: Understanding shapes and patterns even with missing parts |
| Maze Puzzles | Provide maze worksheets for your child to solve. | – Visual Closure: Completing a whole maze with some missing lines – Visual Sequential Memory: Following a specific path or sequence through the maze |
Incorporating Visual Aids and Environmental Adjustments

Creating a visually supportive learning environment can significantly enhance your child’s visual perception skills. Here are some practical adjustments you can make to help them thrive:
1. Visual Cues and Directional Arrows
- Tip: Use colorful stickers, dots, or arrows to guide your child.
- Example Applications:
- Starting Point: Mark the starting side of the page to show where writing or reading should begin.
- Letter Formation: Use arrows to indicate how letters or numbers should be formed.
- Benefit: Visual cues help children stay organized, find their starting points, and write with proper alignment.
2. Organize a Clutter-Free Space
- Tip: Create a tidy, distraction-free area for learning and playing.
- Steps to Achieve This:
- Designated Storage: Provide bins or shelves for toys, school supplies, and books.
- Desk Position: Place the child’s desk in an area with fewer visual distractions (e.g., away from windows or bulletin boards).
- Minimalistic Decor: Keep walls around the desk simple, avoiding overly bright or busy decorations.
- Benefit: A clear workspace minimizes visual overload, enabling your child to focus better on tasks like reading and writing.
3. Highlighted Lines and Boundaries
- Tip: Use highlighters, markers, or tape to define boundaries and guide alignment.
- Example Applications:
- Writing Lines: Highlight the lines on writing sheets to help with letter alignment.
- Boundaries for Tasks: Outline coloring areas, mazes, or cutting tasks using colored tape or markers.
- Benefit: Clearly marked lines improve your child’s ability to maintain neatness in writing and follow task boundaries.
4. Break Tasks into Manageable Steps
- Tip: Divide large or complex tasks into smaller steps.
- Example Applications:
- Puzzles: Present one piece at a time or cover unneeded pieces.
- Worksheets: Split math or reading worksheets into sections using sticky notes or colored paper.
- Benefit: Breaking tasks down makes them less overwhelming, helping your child build confidence and stay focused.
5. Graph Paper and Templates
- Tip: Use graph paper for math problems or templates for writing practice.
- Example Applications:
- Word Spacing: Graph paper can help maintain consistent word spacing.
- Letter Formation: Provide templates for tracing letters, numbers, or shapes.
- Benefit: Structured guidance ensures consistency in writing and spatial alignment.
6. Reduce Visual Stimuli
- Tip: Minimize unnecessary visual stimuli to help your child focus.
- Steps to Achieve This:
- Simple Worksheets: Choose worksheets with only one activity per page and minimal decoration.
- Remove Clutter: Clear off desks and remove distracting items like toys during learning.
- Benefit: Reducing visual stimuli improves attention and allows your child to focus solely on the task at hand.
When to Seek Professional Help
While there are many activities you can try at home to improve visual perception in children, sometimes additional support may be necessary. Here are some signs that it might be beneficial to consult an Occupational Therapist:
1. Persistent Difficulties in School Work:
- Struggling with reading or writing even after practicing activities to enhance visual perception.
- Falling behind in math due to difficulty recognizing numbers or following sequences.
2. Avoidance or Frustration:
- Frequently avoiding activities like drawing, reading, or puzzles.
- Becoming easily frustrated with tasks involving visual perception.
3. Difficulty with Everyday Tasks:
- Challenges with self-care tasks like dressing, matching shoes, or organizing belongings.
- Trouble finding objects in cluttered spaces or following visual instructions.
4. Behavioral Changes:
- Exhibiting low self-esteem or becoming overly anxious about visual tasks.
- Demonstrating behavioral issues in school or at home due to visual perception difficulties.
5. Social Challenges:
- Difficulty recognizing facial expressions and social cues.
- Struggling to participate in group activities or follow games due to spatial issues.
Seeking Help: If you notice these signs, consult an occupational therapist who can provide your child with the specialized support they need. Therapy can include personalized exercises to strengthen visual perception skills and practical strategies to help your child with everyday tasks.
Conclusion
Supporting visual perceptual skills is essential for your child’s development. By recognizing the signs of visual perception difficulties, you can help your child through simple, fun activities like scavenger hunts, memory games, and sorting exercises. These activities can easily fit into your daily routine and significantly improve your child’s reading, writing, and playing ability. Adjusting their learning environment with visual aids and minimizing distractions will also boost their focus and confidence.
Remember to be patient and consistent. These efforts will positively impact your child’s learning, independence, and social skills. If your child continues to struggle, consider seeking professional help.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is visual perception in children?
Visual perception is the brain’s ability to interpret and understand what the eyes see. It involves recognizing shapes, patterns, colors, and spatial relationships. These skills help children with reading, writing, playing games, and completing everyday tasks.
2. How can I improve my child’s visual perception skills at home?
You can improve your child’s visual perception skills through simple activities like scavenger hunts, memory games, dot-to-dot puzzles, and sorting exercises. Adjusting their learning environment with visual aids and reducing clutter can also help.
3. What are the signs of visual perception difficulties in children?
Common signs include:
- Confusing similar-looking letters like “b” and “d.”
- Trouble completing puzzles or dot-to-dot worksheets.
- Losing place while reading or writing.
- Difficulty following sequences or directions.
4. Why is visual perception important in child development?
Visual perception is crucial for academic success, social interaction, and daily tasks. Strong visual perception skills help children read, write, solve puzzles, recognize faces, and navigate their environment confidently.
5. How can memory games help develop visual perception in kids?
Memory games help improve visual memory and form constancy, enabling children to remember and recognize shapes, patterns, and objects even when their orientation changes. This skill is essential for reading, writing, and identifying differences.
6. What activities help develop visual perception in kids?
Activities that help develop visual perception include:
- Scavenger hunts: Improve figure-ground and visual discrimination.
- Dot-to-dot puzzles: Enhance visual closure and sequential memory.
- Sorting games: Strengthen visual discrimination and constancy skills.
- Memory games: Boost visual memory and form constancy.
7. When should I consult an Occupational Therapist for my child’s visual perception issues?
Consider consulting an Occupational Therapist if your child:
- Struggles with reading or writing despite regular practice.
- Avoids tasks like puzzles, drawing, or reading.
- Shows frustration with visual tasks or daily activities.
- Exhibits low self-esteem or behavioral issues related to visual tasks.
8. How does Wellness Hub support children with visual perception challenges?
Wellness Hub provides comprehensive pediatric speech therapy and occupational therapy services. Our experts guide parents with practical strategies and personalized therapy to help children improve their visual perception skills.
9. Can visual perception skills impact my child’s self-esteem?
Yes, children with visual perception difficulties may struggle with reading, writing, and playing games, leading to frustration and low self-esteem. Supporting these skills through fun activities and therapy can improve their confidence and overall well-being.
10. What role does Occupational Therapy play in improving visual perception skills?
Occupational Therapy helps identify specific visual perception challenges and provides personalized exercises to strengthen these skills. An Occupational Therapist can guide your child through targeted activities and strategies to improve reading, writing, and daily tasks. Visit Wellness Hub’s section on Pediatric Speech Therapy here for more details on therapy options.
About the Author:
Anuradha Karanam
Speech-language pathologist (7+ years of experience)
Anuradha Karanam is a skilled speech-language pathologist with over 6 years of experience. Fluent in Tamil, Telugu, Hindi, and English, she specializes in parent counseling, speech sound disorders, fluency assessment, and speech-language evaluations. Anuradha excels at working with children with developmental disorders, offering creative and effective therapy programs. Currently, at Wellness Hub, she holds a BASLP degree and is registered with the RCI (CRR No A85500). Her patience, ambition, and dedication make her a trusted expert in her field.
Connect with Anuradha to learn more about how she can help you or your loved one find their voice.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message









