Understanding Neurodiversity: Signs, Conditions & How to Support Your Child
Last Updated: April 21, 2025
Have you ever felt like your child sees the world a little differently? Maybe they focus deeply on things they love, prefer routines, or learn in ways that don’t match traditional classroom methods. If so, you’re not alone—and you may be seeing signs of neurodiversity.
Neurodiversity is a word that celebrates how every brain is different. Some children are neurotypical, while others are neurodivergent, meaning their brains think, learn, or feel differently. In this guide, we’ll explore what neurodiversity really means, the types of neurodivergent conditions, and how you—as a parent—can support your child with understanding and confidence.
What is Neurodiversity? Embracing Different Ways of Thinking
Have you ever noticed how some people think in incredibly unique ways—solving problems differently, noticing tiny details others miss, or needing routines that make them feel safe? That’s the power of neurodiversity.
Put simply, neurodiversity means that not all brains work the same way—and that’s okay. It’s a term that recognizes and respects the different ways our brains are wired. Just like we all have different fingerprints, we also have different thinking patterns, strengths, and challenges.
Some people are called neurotypical—their brain functions in ways that are considered “standard” by society. Others are neurodivergent—their brains process, react, and interpret the world differently. This can include individuals with:
- Autism
- ADHD
- Dyslexia
- Dyspraxia
- Tourette syndrome
- Learning disabilities
But here’s what matters: neurodivergence is not a problem to fix—it’s a difference to understand and support.
Also read: What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Why Does Neurodiversity Matter?
Recognizing neurodiverse ways of thinking helps us:
- See strengths instead of just challenges
- Build inclusive classrooms, homes, and workplaces
- Support children and adults in reaching their full potential
- Reduce stigma around autism, ADHD, and learning differences
Whether it’s a child who sees the world in patterns or an adult who brings out-of-the-box ideas to work, embracing neurodiversity benefits everyone.
Understanding Neurodiversity in Simple Terms
If you’ve ever wondered, “What does it mean to be neurodivergent?”—you’re not alone. Many parents, caregivers, and educators are just beginning to explore this important topic. So let’s break it down in a way that’s easy to understand.
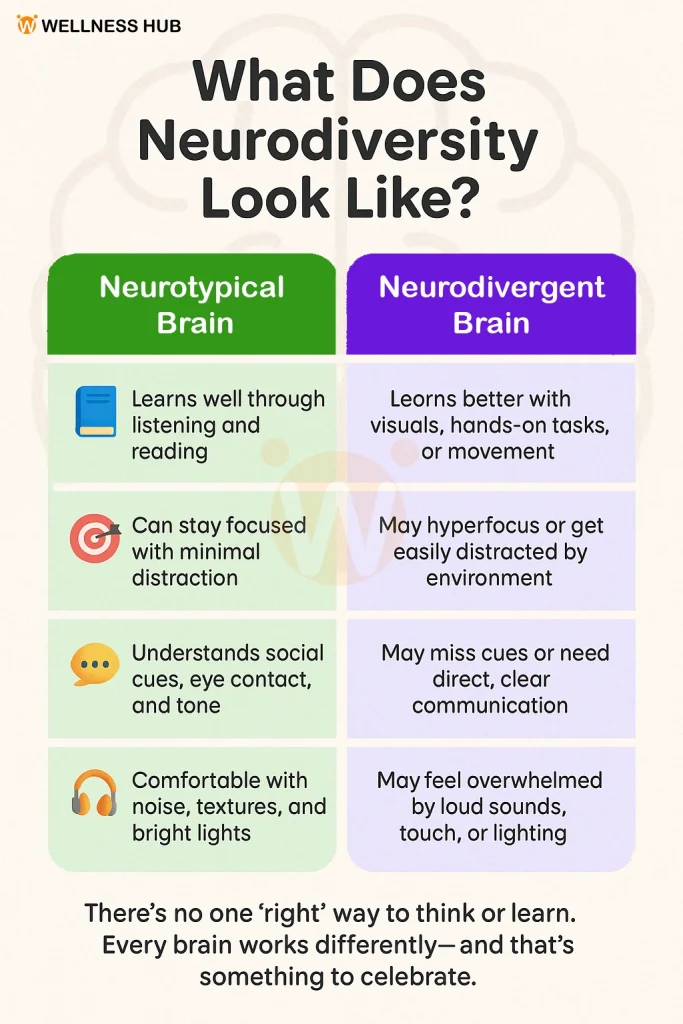
What Does “Neurodivergent” Mean?
Neurodivergent simply means a person’s brain works differently from what is considered typical. These differences can affect how someone:
- Thinks
- Learns
- Focuses
- Communicates
- Processes emotions or sensory input
And guess what? That doesn’t make them any less capable. In fact, many neurodivergent individuals have incredible strengths—like creativity, memory, visual thinking, or deep focus.
Common Neurodiverse Conditions
The term neurodiversity includes a wide range of conditions. Some of the most common include:
| Neurodiverse Condition | Key Traits or Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Autism | Prefers routines, strong focus, may struggle with social interaction |
| ADHD | High energy, distractibility, creative thinking, impulsivity |
| Dyslexia | Difficulty with reading or spelling, strong verbal or visual skills |
| Dyspraxia | Challenges with motor coordination, often bright and resilient |
| Tourette Syndrome | Involuntary tics, often paired with high intelligence or humor |
| Learning Disabilities | Trouble with reading, writing, or math, but capable of learning in different ways |
Different Ways of Thinking and Learning
Being neurodiverse means that traditional learning or communication methods might not always work. But that doesn’t mean a child or adult is any less intelligent or capable. It just means they may need:
- More visual aids or hands-on learning
- Breaks to manage sensory overwhelm
- Clearer routines and transitions
- One-on-one support, like speech therapy or emotional coaching
And this is exactly where supportive environments matter.
Why is Neurodiversity Important in Today’s World?
When we talk about diversity, we often think about culture, language, or background. But there’s another kind of diversity that matters just as much—the diversity of our minds.
In simple terms, neurodiversity reminds us that people don’t all think, learn, or feel the same way—and that’s not only okay, it’s valuable.
Different brains = different strengths = better ideas.
Benefits of Neurodiversity in Schools, Workplaces, and Homes
When we recognize and support neurodiverse individuals, we make space for creativity, empathy, and new ways of solving problems.
At Schools:
- Neurodiverse students bring unique perspectives to the classroom
- Creative thinkers often excel in art, science, or technology
- With the right support (like speech therapy or visual learning tools), they can thrive
In Workplaces:
- Neurodivergent adults can be detail-focused, innovative, and deeply passionate
- Many companies now see neurodiverse hiring as a strength, not a challenge
- Teams become stronger when different thinking styles are welcomed
In Homes:
- Understanding a child’s thinking style can reduce stress for parents
- Embracing routines, visual aids, and emotional coaching can make daily life easier
- Families grow more patient and connected when they understand neurodiversity
Types of Neurodivergent Conditions You Should Know
Neurodiversity isn’t just one thing—it includes a wide range of conditions that affect how people think, feel, and learn. Each neurodivergent condition comes with its own challenges, but also incredible strengths. Let’s explore three of the most common ones:

Autism and Neurodiversity
Autism, or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects communication, behavior, and social interaction. But that’s just one side of the story.
Many autistic individuals:
- Notice details others miss
- Think in pictures or patterns
- Have deep focus on topics they love
- Prefer predictable routines
They may also experience:
- Sensory sensitivities (to sound, light, or texture)
- Difficulty with changes in routine
- Challenges in reading social cues
What’s important to remember is this: autistic people don’t lack intelligence or empathy—they simply experience the world in a different way. With understanding and the right tools (like visual schedules or therapy support), they can thrive in school, work, and relationships.
ADHD and Neurodivergent Thinking
ADHD, or Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, is another form of neurodivergence that affects attention, impulse control, and energy levels.
Common signs include:
- Trouble focusing for long periods
- High energy or restlessness
- Difficulty sitting still or waiting turns
- Acting on impulse without thinking
But here’s the positive side:
ADHD brains are often creative, energetic, and full of ideas. Many individuals with ADHD:
- Thrive in fast-paced environments
- Excel at brainstorming and big-picture thinking
- Perform well with hands-on or movement-based tasks
Simple strategies—like using timers, breaking tasks into small steps, or incorporating movement breaks—can make a huge difference. And at Wellness Hub, we offer expert-backed tools and counseling that help children and families navigate ADHD with confidence.
Learning Disabilities and Neurodiverse Strengths
Not all neurodivergent conditions are about behavior or energy. Some affect how people learn, read, or write. These are often called specific learning disabilities, and they include:
- Dyslexia – challenges with reading or spelling
- Dyspraxia – difficulty with motor coordination
- Dyscalculia – trouble with math concepts
These challenges don’t mean a child isn’t smart. In fact, many children with learning disabilities are:
- Great at storytelling or oral communication
- Highly visual or artistic
- Strong in logic, memory, or spatial skills
What helps most is a strength-based approach—focusing on what the child can do and building on that. Tailored interventions, such as reading programs or occupational therapy, can turn struggle into success.
Embracing Neurodiversity at Home, School, and Work
Supporting neurodiverse individuals doesn’t mean having all the answers. It means creating spaces where they can feel safe, understood, and accepted—whether at home, in the classroom, or in the workplace.
Let’s look at how small changes in each of these environments can make a big difference.
How Parents Can Support Neurodiverse Children
If you’re a parent of a neurodivergent child, you’ve probably asked yourself, “How can I best support my child at home?” The good news? Support doesn’t need to be complicated.
Here are some practical, gentle ways to help:
- Stick to routines: Predictable daily structures help reduce anxiety
- Use visual tools: Charts, picture schedules, and timers work well for kids who learn visually
- Create sensory-friendly spaces: Calming corners, weighted blankets, or noise-canceling headphones can help regulate emotions
- Break tasks into steps: One thing at a time is easier for overwhelmed minds
- Celebrate their strengths: Focus on what your child does well—even if it’s different from the “norm”
At Wellness Hub, we offer therapy services, home routines, and parenting support tools to help you build an environment that supports—not stifles—your child’s growth.
Inclusive Education for Neurodivergent Students
A child’s learning environment plays a huge role in their development. For neurodivergent students, traditional classrooms may feel overwhelming—but a few key adjustments can go a long way.
What helps in inclusive classrooms:
- Flexible seating or quiet spaces
- Extra time during tests or assignments
- Visual instructions instead of only verbal ones
- Sensory breaks to reset and recharge
- Therapy support, such as:
- Speech therapy for communication challenges
- Occupational therapy to build motor and self-help skills
By working together—parents, teachers, and therapists—we can build learning environments that work for the child, not against them.
Neurodiversity in the Workplace
Neurodivergent individuals often bring fresh perspectives, deep focus, and problem-solving skills to the workplace. Companies are starting to realize that having a mix of brain types isn’t a challenge—it’s a competitive advantage.
Benefits of a neurodiverse workforce:
- Greater innovation and creativity
- Unique solutions to complex problems
- Loyalty and attention to detail
- Higher engagement when placed in the right roles
How employers can be more inclusive:
- Offer flexible work options (like quiet spaces or remote work)
- Use clear communication—written + verbal
- Provide training for managers on neurodiversity awareness
- Focus on strengths, not just job titles
Conclusion
Every brain is different—and that’s something to celebrate. Neurodiversity means we all think, learn, and feel in our own unique ways. Whether your child has autism, ADHD, or a learning difference, remember: different doesn’t mean less. At Wellness Hub, we’re here to support you with online therapy, speech support, and parenting tools designed for real families. Don’t wait to get help—reach out today and take the first step toward understanding and growth. Let’s embrace every mind, every strength, every story.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What does neurodiversity mean in simple words?
Neurodiversity means that people’s brains work in different ways. Some may think, learn, or feel things differently—and that’s perfectly okay. It includes conditions like autism, ADHD, and dyslexia.
2. Is my child neurodivergent if they don’t learn like others?
Yes, if your child learns, focuses, or communicates differently, they may be neurodivergent. This can include things like needing routines, having speech delays, or struggling in school—but also having unique strengths.
3. What are common signs of neurodiversity in children?
Some signs include speech delay, difficulty with focus, sensitivity to sound or touch, or needing strong routines. Every child is different, so it’s best to talk to a professional.
4. How is neurodiversity different from a disability?
Neurodiversity is not about being disabled—it’s about being different. Some neurodivergent people may need support, but they also have amazing skills and strengths.
5. What are the types of neurodiverse conditions?
Common types include:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- ADHD
- Dyslexia
- Dyspraxia
- Tourette Syndrome
- Learning Disabilities
6. Can speech therapy help neurodivergent children?
Yes! Speech therapy can improve communication, reduce frustration, and help children express their needs clearly—especially for kids with autism or speech delays.
7. How can I support my neurodivergent child at home?
Use visual schedules, stick to routines, and give simple instructions. Most importantly, be patient and celebrate your child’s strengths. You can also try therapy tools from Wellness Hub.
8. Should I get my child tested for a learning difficulty?
If your child struggles with reading, writing, or following directions, a test can help. You can try our Speech and Language Communication Tests to get started.
9. Can neurodiverse kids do well in school?
Absolutely! With the right support—like classroom changes, therapy, or extra time—many neurodiverse children thrive in school and beyond.
10. Where can I find help for my child with autism or ADHD?
You can start with a free consultation at Wellness Hub. We offer therapy, parenting help, and support designed for Indian families.
About the Author:
Shilpa Deshpande
Shilpa Deshpande is a skilled speech-language pathologist with over 14 years of experience. Fluent in Kannada, Telugu, Hindi, and English, she specializes in parent counseling, speech sound disorders, fluency assessment, and speech-language evaluations. Shilpa excels at working with children with developmental disorders, offering creative and effective therapy programs. Currently, at Wellness Hub, she holds a BASLP degree and is registered with the RCI. Her patience, ambition, and dedication make her a trusted expert in her field.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message








