ABA vs. Occupational Therapy: What’s the Difference?
By Wellness Hub
Last Updated: July 6, 2024
Navigating the landscape of therapeutic options for children on the autism spectrum can be overwhelming for parents and caregivers. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) and Occupational Therapy (OT) stand out as two leading therapies, each with distinctive approaches tailored to meet the varied needs of these children. Understanding the nuances between ABA’s structured behavioral modification techniques and OT’s focus on enhancing daily living skills through engaging activities is essential. This guide will help you discern which therapy aligns best with your child’s unique developmental challenges, enabling you to make well-informed decisions that foster optimal growth and progress.
What is ABA Therapy?
Definition
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a well-established approach designed to improve specific behaviors in children, particularly those with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and developmental delays. ABA focuses on the principles of behaviorism, emphasizing the observation and modification of behaviors to enhance learning and development.
Methods
ABA therapy employs various methods to help children learn new skills effectively. Two primary techniques used in ABA are shaping and chaining.
- Shaping: This method involves reinforcing successive approximations of a desired behavior. Essentially, it starts with the child’s current ability and gradually encourages behaviors that bring them closer to the overall goal. For example, if a child is learning to communicate, initial efforts at vocalizing might be rewarded, gradually progressing to forming words and sentences.
- Chaining: This technique breaks down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps. Each step is taught individually and linked together to form the complete task. For instance, a daily living skill like brushing teeth can be divided into steps such as picking up the toothbrush, applying toothpaste, and brushing in a sequence.
Also Read: Understanding and Parenting an Autistic Child: Guide and Tips
Goals
ABA therapy aims to improve various aspects of a child’s life, focusing on:
- Communication: Enhancing verbal and non-verbal communication skills to express needs and interact with others.
- Daily Living Skills: Teaching essential activities such as dressing, eating, and personal hygiene.
- Social Interactions: Developing the ability to interact appropriately with peers and adults, fostering better social relationships.
Approach
A key feature of ABA therapy is its play-based approach, which makes the learning process engaging and enjoyable for children. By incorporating play, therapists can create a natural learning environment where children feel comfortable expressing themselves. Additionally, ABA therapy often involves modifying the child’s environment to encourage positive behaviors and reduce obstacles to learning.
What is Occupational Therapy?
Definition
Occupational Therapy (OT) is a holistic and client-centered approach designed to help individuals engage in meaningful activities across their lifespan. For children, this often means using play as a primary method to enhance their skills and improve their ability to participate in daily activities.
Methods
Occupational therapists employ a variety of methods to support children’s development, including:
- Play: Play is used to develop essential skills in a fun and engaging way. Through structured play, children can improve their fine motor skills, sensory processing, and emotional regulation.
- Sensory Integration: This method helps children better process and respond to sensory information, which can improve their ability to function in different environments.
- Emotional Regulation: Therapists use specific strategies to help children manage their emotions, reducing anxiety and frustration.
Goals
The primary goals of Occupational Therapy are to promote:
- Independence in Daily Activities: Helping children master skills needed for everyday tasks such as dressing, eating, and personal hygiene.
- Fine Motor Skills: Improving the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, which is essential for tasks like writing and using utensils.
- Self-Care: Enabling children to take care of their personal needs with minimal assistance, fostering a sense of autonomy and confidence.
Approach
Occupational Therapy is distinguished by its client-centered approach, which means that therapy is tailored to the individual needs and goals of each child. Therapists use a variety of treatment strategies, including adaptive equipment, therapeutic exercises, and activities that are meaningful to the child. This personalized approach ensures that therapy is effective and relevant to the child’s unique circumstances.
Similarities Between ABA and Occupational Therapy
1. Common Goals
Both Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy and Occupational Therapy (OT) share a common mission: to help children develop essential skills and behaviors. These therapies aim to enhance the overall well-being of children, particularly those with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and developmental delays. By focusing on improving various skills, both therapies strive to foster greater independence and better quality of life for children.
2. Play-Based Approach
A significant similarity between ABA and OT is their use of play as a key component of therapy. Play is a natural and effective way for children to learn and develop new skills. In both ABA and OT, play-based activities are used to make the therapy sessions engaging and enjoyable, which helps children stay motivated and invested in the learning process.
3. Focus on ASD
Both ABA and OT are highly effective for children with autism spectrum disorder. These therapies are designed to address the unique challenges faced by children with ASD, helping them improve communication, social interactions, and daily living skills. By targeting these areas, ABA and OT provide essential support for children with ASD and their families.
4. Task Breakdown
Another common feature of ABA and OT is their approach to breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable steps. This method helps children master each component of a task before moving on to the next, making it easier for them to learn complex skills. Whether it’s learning a new behavior in ABA or developing fine motor skills in OT, breaking tasks into smaller steps ensures that children can achieve success at each stage of their development.
Differences Between ABA and Occupational Therapy
1. Philosophies
Occupational Therapy (OT) takes a holistic and client-centered approach. This means therapists focus on the entire person and tailor their interventions to the individual’s unique needs, preferences, and goals. OT addresses physical, emotional, and cognitive aspects of a person’s life to promote overall well-being and independence.
In contrast, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is rooted in behaviorism, which focuses on observable behaviors and how they can be modified through reinforcement and environmental changes. ABA aims to improve specific behaviors by systematically applying principles of learning and conditioning.
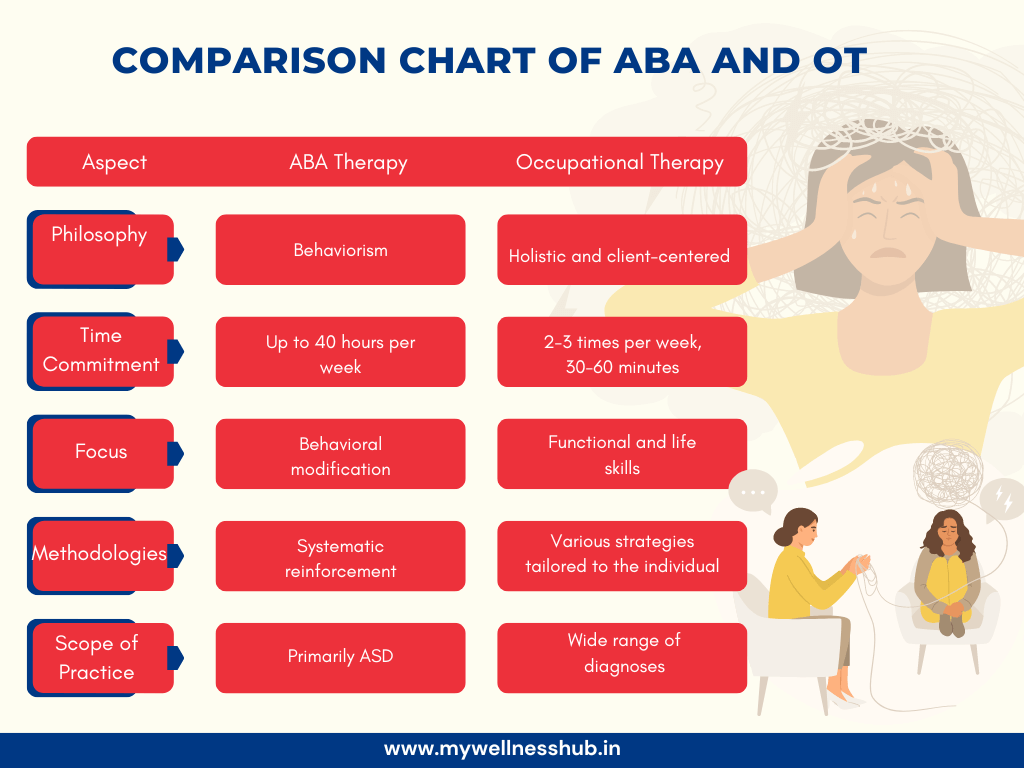
2. Time Commitment
ABA therapy is known for its intensive nature. It can be conducted for up to 40 hours per week, often requiring significant time and effort from both the child and the caregivers. This high level of commitment is designed to maximize learning opportunities and ensure consistent reinforcement of desired behaviors.
On the other hand, Occupational Therapy typically requires less time per week. Sessions are often scheduled two to three times a week for 30 to 60 minutes each. This difference in time commitment makes OT more flexible for families who may have other obligations or prefer a less intensive therapy schedule.
3. Target Skills
ABA focuses primarily on behavioral modification. It aims to improve socially significant behaviors, such as communication, social skills, and adaptive living skills. The goal is to increase positive behaviors and reduce those that are harmful or interfere with learning.
OT, however, targets a broader range of skills. These include fine motor skills, sensory processing, self-care tasks, and emotional regulation. The aim is to help individuals perform daily activities independently and effectively, improving their overall quality of life.
Methodologies
ABA uses systematic reinforcement techniques to encourage desired behaviors. This involves identifying specific behaviors to increase or decrease, and then applying consistent reinforcement to shape these behaviors. Techniques such as positive reinforcement, shaping, and chaining are commonly used.
In contrast, OT employs a variety of strategies tailored to the individual. These might include sensory integration techniques, therapeutic exercises, and the use of adaptive equipment. The goal is to support the individual’s ability to engage in meaningful activities and improve their functional capabilities.
Scope of Practice
The scope of Occupational Therapy is broad, addressing a wide range of diagnoses beyond autism spectrum disorder (ASD). OT can benefit individuals with physical disabilities, developmental delays, mental health issues, and other conditions that affect their ability to perform daily tasks.
ABA, while versatile, is primarily used for individuals with ASD. It is considered one of the most effective therapies for autism, focusing on reducing problematic behaviors and teaching new skills that improve social interactions and independence.
Differences Between ABA and Occupational Therapy
| Feature | ABA Therapy | Occupational Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Behavior modification through reinforcement | Client-centered, focuses on meaningful activities |
| Techniques | Shaping, chaining | Sensory integration, adaptive equipment |
| Goal Setting | Specific behavior goals | Functional independence |
| Typical Duration | 20-40 hours per week | 1-2 hours per week |
| Ideal For | Behavioral issues, social skills | Fine motor skills, sensory issues |
Benefits of ABA Therapy
Social Skills
One of the most significant benefits of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is the improvement in social skills. Children undergoing ABA therapy often experience enhanced social interactions and better peer relationships. By focusing on specific social behaviors and reinforcing positive interactions, ABA helps children learn how to communicate effectively, understand social cues, and engage with others in meaningful ways. This development is crucial for building friendships and integrating into social settings.
Emotional Regulation
ABA therapy also plays a vital role in helping children manage their emotions. Through various techniques, children learn to identify their emotions and develop strategies to cope with feelings of frustration, anger, or anxiety. By providing a structured environment and consistent reinforcement, ABA therapists help children gain control over their emotional responses, leading to a more stable and positive emotional state.
Independence
Another key advantage of ABA therapy is the increased ability of children to perform daily living activities independently. ABA focuses on teaching essential life skills such as dressing, eating, and personal hygiene. By breaking down these tasks into smaller, manageable steps and reinforcing each step, children gradually gain the confidence and competence needed to perform these activities on their own. This independence is a significant milestone in their overall development and quality of life.
Parental Involvement
ABA therapy also encourages parental involvement, which is crucial for the success of the therapy. Parents are often trained to implement ABA techniques at home, ensuring consistency and reinforcement of positive behaviors outside therapy sessions. This involvement not only empowers parents but also strengthens the parent-child relationship. It provides parents with the tools and knowledge to support their child’s progress and celebrate their achievements together.
Benefits of Occupational Therapy
Functional Skills
One of the primary benefits of Occupational Therapy (OT) is the improvement in functional skills. OT helps children develop fine motor skills, which involve the small muscles in the hands and fingers. These skills are essential for tasks such as writing, buttoning clothes, and using utensils. Additionally, OT enhances hand-eye coordination, which is crucial for activities like playing sports and drawing. By focusing on these areas, OT helps children perform everyday tasks with greater ease and precision.
Life Skills
Occupational Therapy also significantly enhances a child’s ability to perform self-care tasks. These life skills include dressing, bathing, grooming, and feeding. OT therapists work with children to break down these activities into manageable steps, teaching them how to complete each step independently. This training not only boosts the child’s confidence but also fosters a sense of autonomy and self-reliance, essential for their overall development and integration into daily routines.
Sensory Processing
Another vital area where OT makes a difference is in sensory processing. Many children with developmental delays or autism spectrum disorder experience sensory sensitivities, making it challenging to process and respond to sensory information. OT helps children manage these sensitivities through sensory integration techniques. By exposing children to various sensory experiences in a controlled and gradual manner, OT helps them develop better coping strategies and responses, reducing anxiety and improving their ability to function in different environments.
Overall Well-being
The cumulative effect of improved functional skills, life skills, and sensory processing is an enhanced overall well-being. Children who receive Occupational Therapy often experience a better quality of life through increased independence and the ability to participate in a wider range of activities. This holistic improvement not only benefits the child but also brings relief and satisfaction to their families, knowing that their child is gaining the skills necessary to thrive.
Choosing the Right Therapy for Your Child
Individual Needs
When selecting the right therapy for your child, it’s crucial to consider their specific needs and goals. Every child is unique, and what works for one may not be as effective for another. Start by assessing your child’s strengths and challenges. For instance, if your child struggles primarily with behavioral issues and social interactions, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) might be particularly beneficial. Conversely, if fine motor skills or sensory sensitivities are the main concerns, Occupational Therapy (OT) could be more suitable. Understanding these nuances will help tailor a therapy plan that directly addresses your child’s individual needs.
Combination Approach
In many cases, a combination of ABA and OT can provide a comprehensive approach to therapy. While ABA focuses on behavioral modifications and social skills, OT targets functional abilities and sensory processing. By integrating both therapies, you can address a broader range of your child’s developmental needs. For example, ABA can help improve your child’s ability to communicate and interact with peers, while OT can enhance their ability to perform daily tasks independently. This combined approach often leads to more significant and holistic improvements.
Professional Guidance
Navigating the landscape of therapy options can be overwhelming, but you don’t have to do it alone. Consulting with professionals who specialize in child development can provide invaluable insights and guidance. Therapists, pediatricians, and special education professionals can help you understand the nuances of ABA and OT, and how each might benefit your child. They can also assist in developing a personalized therapy plan that aligns with your child’s unique needs and your family’s goals.
At Wellness Hub, we understand the complexities involved in choosing the right therapy for your child. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to helping you make informed decisions that best support your child’s growth and development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey to selecting the appropriate therapy for your child is intricate yet crucial for their development. At Wellness Hub, we’re committed to easing this process by offering expert advice and support tailored to your child’s specific needs. With a team of seasoned professionals, we ensure that you are well-equipped to make decisions that foster your child’s progress and well-being. Let us guide you through this path, helping you navigate the options with confidence and clarity, for the brighter future your child deserves.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the main difference between ABA and Occupational Therapy?
ABA focuses on modifying specific behaviors through systematic reinforcement, while Occupational Therapy takes a holistic approach to improve functional and life skills.
2. Can ABA and Occupational Therapy be used together?
Yes, combining ABA and Occupational Therapy can provide comprehensive support, addressing both behavioral modifications and the development of functional skills.
3. How do I decide between ABA and Occupational Therapy for my child?
Consider your child’s specific needs and goals. If your child struggles with behaviors and social interactions, ABA might be more suitable. If fine motor skills or sensory sensitivities are a concern, OT could be beneficial. Consulting with a professional can help you make an informed decision.
4. How intensive is ABA therapy compared to Occupational Therapy?
ABA therapy can be very intensive, often up to 40 hours per week. In contrast, Occupational Therapy typically requires less time, with sessions often scheduled two to three times a week for 30 to 60 minutes each.
5. What skills does Occupational Therapy focus on?
Occupational Therapy focuses on developing fine motor skills, sensory processing, self-care tasks, and overall functional abilities to enhance a child’s independence and quality of life.
6. Is ABA therapy effective for children with autism?
Yes, ABA is considered one of the most effective therapies for children with autism, helping improve communication, social skills, and adaptive behaviors.
7. How can parents be involved in ABA therapy?
Parents are often trained to implement ABA techniques at home, ensuring consistency and reinforcement of positive behaviors outside therapy sessions.
8. What are the benefits of combining ABA and Occupational Therapy?
Combining ABA and OT can address a wider range of developmental needs, providing comprehensive support that improves both behavioral and functional skills.
9. What should I look for in a therapy provider for my child?
Look for experienced professionals who specialize in child development and offer a personalized approach to therapy. It’s also important to find a provider who encourages parental involvement and offers clear communication about progress and goals.
10. How can Wellness Hub help my child with therapy needs?
At Wellness Hub, we offer a range of therapies, including ABA and Occupational Therapy, tailored to the unique needs of each child. Our experienced team can help you create a personalized plan to support your child’s development and overall well-being.
About Author
Prapoorna Mangalampalli
M.Sc., M.A., (Dual Masters in Psychology and Senior Content Developer) – Counselor (6+ years of experience)
Prapoorna is a skilled counselor with dual Master’s degrees in Psychology and English. With more than six years of professional experience, she specializes in providing various types of counseling, including online Therapy , Marital , Relationship, child, family, and career counseling. Prapoorna is part of the Wellness Hub team, where she contributes significantly to their mission. She values a team-based approach and is committed to innovation, compassion, and the success of her clients. Her diverse educational background and extensive experience enable her to offer insightful and effective counseling services that positively impact individuals and families.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message









