Understand Aphasia and Apraxia: Improve Speech
Last Updated: January 23, 2024
Language is at the heart of human connection, essential for expressing thoughts and emotions. However, conditions like Aphasia and Apraxia can disrupt this fundamental ability, profoundly impacting communication. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between these disorders, their causes, symptoms, and treatments, and how they affect daily life. Our goal is to provide clarity and practical insights to those affected and their support networks, enhancing understanding and management of these challenging conditions. Join us as we navigate the complexities of Aphasia and Apraxia, offering support and solutions for improved communication.
Book Your Online Speech Counselling Now
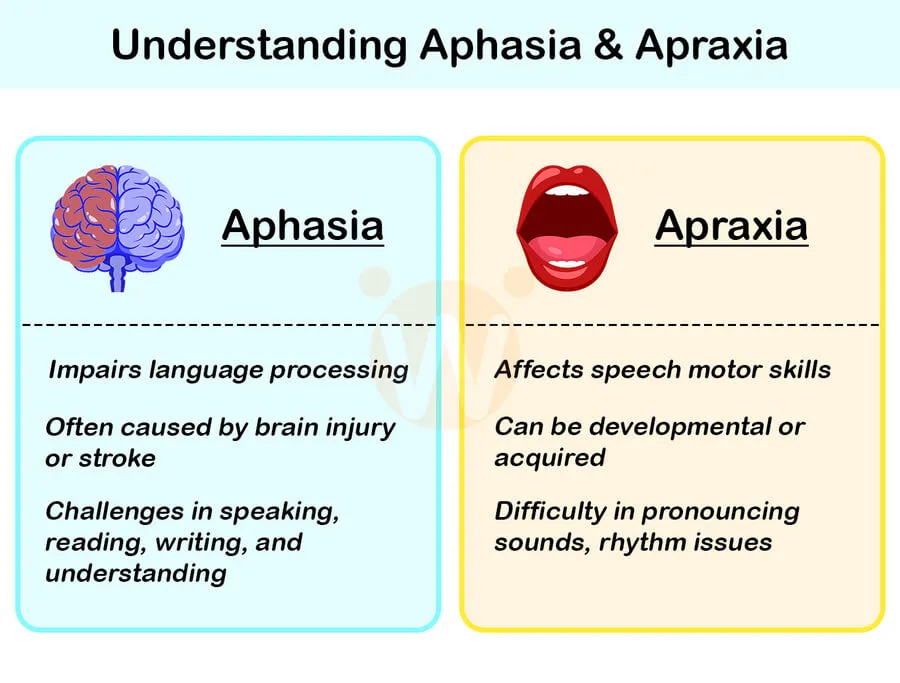
What are Aphasia and Apraxia?
Understanding Aphasia
Aphasia is a language disorder that arises when brain areas responsible for language are damaged, often due to stroke or head injury. This impairment can affect speech, writing, reading, and the ability to understand language. The impact on a person’s communication abilities can vary significantly depending on the type and severity of the aphasia.
Understanding Apraxia of Speech
Apraxia of Speech (AOS) is a motor speech disorder, not a language impairment. It occurs when the brain struggles to coordinate the muscle movements necessary to pronounce sounds, syllables, and words. Unlike aphasia, which involves the processing of language, apraxia affects the ability to plan and execute the physical movements of speech.
Key Points about Apraxia of Speech:
- Speech Production Focus: Apraxia primarily impacts how speech sounds are formed, not the understanding of language. People with apraxia know what they want to say but face difficulty in physically articulating the words.
- Differentiation from Aphasia: While aphasia involves a breakdown in the comprehension or formulation of language, apraxia is purely about the motor skills needed for speaking. This distinction is crucial for effective diagnosis and therapy.
Types and Characteristics
Types of Aphasia
Aphasia can manifest in several forms, each affecting speech and comprehension to different extents. Here’s a closer look at the main types:
- Broca’s Aphasia (Non-fluent Aphasia): This form is characterized by slow, halting speech and difficulty in forming sentences. People with Broca’s Aphasia often understand spoken language well but struggle with speech production and grammar.
- Wernicke’s Aphasia (Fluent Aphasia): Individuals with this type speak in long, complete sentences that lack meaning. They often produce unnecessary or made-up words and have significant difficulty understanding spoken language.
- Global Aphasia: This is the most severe form, combining extensive impairments in speaking, understanding, reading, and writing. Communication may be limited to very few words or phrases.
- Anomic Aphasia: People with Anomic Aphasia can speak fluently in grammatically correct sentences but frequently encounter word-finding interruptions. Their ability to understand language remains intact.
Types of Apraxia
Apraxia of Speech is primarily seen in two forms, each presenting unique challenges:
- Acquired Apraxia of Speech: Often occurring in adults, this condition follows a neurological event, such as a stroke or head injury. Symptoms include difficulty forming consistent speech sounds, struggling with speech rhythm and timing, and generally knowing what they want to say but not being able to say it correctly.
- Childhood Apraxia of Speech (CAS): CAS is a motor speech disorder that emerges early in childhood and affects a child’s ability to speak clearly and consistently. While the exact causes of CAS are not fully understood, genetic factors may play a role, with some evidence pointing to hereditary links. CAS is not as common as other speech disorders, but it requires early and specific intervention for improvement.
Also Read: Speech Sound Disorders: Causes, Treatment and Strategies
Causes and Diagnosis
Causes of Aphasia
Aphasia results from damage to the parts of the brain responsible for language. This damage can stem from several causes:
- Stroke: The most common cause of aphasia, a stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, leading to brain cell damage that affects language capabilities.
- Brain Injuries: Traumatic brain injuries, such as those from accidents or falls, can cause localized damage to language-processing areas of the brain.
- Tumors: Brain tumors can pressure or destroy brain tissue, including areas critical for language processing.
- Neurological Conditions: Diseases like Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia can progressively impair the brain’s ability to process and produce language.
Know more about our article on Aphasia: Causes, Symptoms, Types and Treatment
Causes of Apraxia
Apraxia of Speech is primarily caused by neurological damage that disrupts the brain’s ability to coordinate the muscle movements necessary for speaking:
- Brain Damage: Damage to the brain’s motor planning areas, often due to stroke or traumatic brain injury, can lead to acquired Apraxia of Speech.
- Genetic Considerations: Particularly in Childhood Apraxia of Speech (CAS), genetic factors might play a role, with some cases showing familial patterns that suggest a hereditary component.
- Neurodevelopmental Factors: Early developmental issues can affect the brain’s normal speech-motor control development, leading to apraxia in children.
Diagnosing Aphasia and Apraxia
The diagnosis of Aphasia and Apraxia involves a comprehensive assessment by healthcare professionals:
- Role of Healthcare Professionals: Speech-language pathologists play a pivotal role in diagnosing and treating both Aphasia and Apraxia. Neurologists may also be involved when underlying neurological conditions are suspected.
- Diagnostic Tests: These may include imaging tests like MRI or CT scans to view the brain’s structure and identify any abnormalities. For Apraxia, specific motor speech evaluations are conducted.
- Assessments Used: Standardized speech and language tests assess various aspects of language comprehension and speech production. These tests help determine the type and severity of Aphasia or Apraxia and guide the treatment planning.
Treatment Strategies and Management
Treatment of Aphasia
The treatment of Aphasia primarily revolves around speech and language therapy, which aims to help regain language skills and improve communication abilities. Here are key strategies employed in the treatment:

- Individualized Therapy: Each case of Aphasia is unique, so personalized therapy plans are crucial. Speech-language pathologists tailor interventions based on the specific needs and abilities of the individual, focusing on relearning language and speech skills.
- Group Therapy: Participating in group therapy sessions allows individuals with Aphasia to practice communication skills in a supportive setting, facilitating social interaction and practical application of language skills.
- Use of Adaptive Technologies: Technologies such as communication aids, speech-generating devices, and specialized software can help individuals compensate for language difficulties. These tools are designed to enhance communication, whether through augmenting speech production or providing visual and textual cues to aid comprehension.
- Incorporating Multimodal Communication: Therapy often includes gestures, writing, drawing, and the use of pictures to support speech and help convey meaning, expanding the ways in which individuals can express themselves.
Management of Apraxia
Managing Apraxia involves specific techniques aimed at improving the coordination of muscle movements necessary for speech. Here’s how it’s approached:
- Repetitive Speech Exercises: These exercises help strengthen the neural pathways involved in planning and producing speech, making the production of words and phrases more automatic and less effortful.
- Motor Planning and Execution Training: This includes practicing the movement patterns that produce speech sounds, improving the consistency and clarity of speech.
- Use of Supportive Technologies: Various software and apps are available that provide visual and auditory feedback to individuals, allowing them to practice and refine their speech in real-time.
- Melody-Based Therapy: For some, using melody and rhythm can improve speech fluidity and articulation, a technique particularly useful in cases where Apraxia coexists with Aphasia.
Aphasia vs. Apraxia – Key Differences
Understanding Aphasia and Apraxia can be simpler when we lay out their differences side by side:
| Aspect | Aphasia | Apraxia |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Impact | Language Processing (understanding and forming language) | Motor Planning (coordinating muscles for speech) |
| Key Symptoms | Difficulty with speaking, understanding, reading, and writing | Difficulty pronouncing sounds, inconsistent speech errors |
| Causes | Often due to stroke or brain injury | Typically, due to brain damage, it can be developmental in children |
| Treatment Focus | Language relearning and communication strategies | Speech-motor coordination and practice |
| Speech Characteristics | May use wrong words or incomplete sentences | Struggles with sound production, rhythm, and flow of speech |
Living with Aphasia and Apraxia
Living with Aphasia or Apraxia can significantly impact daily life and social interactions. Here’s a structured overview in bullet points and table format to highlight the challenges and personal stories that humanize these conditions.
Daily Life Challenges
- Communication Frustrations:
- Difficulty with reading, writing, and understanding complex information.
- Challenges in performing daily tasks that require verbal instructions or interaction.
- Social Interactions:
- Struggles with following conversations in social settings.
- Fear of embarrassment or misunderstanding, leading to social withdrawal.
Personal Stories and Case Studies
| Name | Condition | Challenges | Support and Progress |
|---|---|---|---|
| John | Aphasia | Lost ability to teach and engage socially due to communication barriers. | Through speech therapy and support groups at Wellness Hub, regained confidence and began participating in community activities. |
| Emma | Apraxia | Difficulty in speaking clearly; was not speaking as much as peers at age three. | Benefited from early intervention and regular therapy, improving speech clarity and confidence over time. Parents active in online support communities. |
Conclusion
Understanding Aphasia and Apraxia can be tough, but with the right help, life gets easier. Whether you’re dealing with these speech challenges yourself or supporting someone who is, remember: you’re not alone. At Wellness Hub, we offer tools and guidance to make communication smoother and more enjoyable. Dive into our Resource Section for easy tips and expert advice that make a real difference. Together, we can overcome these challenges and help everyone find their voice again.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the main difference between Aphasia and Apraxia?
Aphasia primarily affects language processing abilities, impacting speaking, reading, writing, and understanding. Apraxia, on the other hand, is a motor speech disorder where the challenge lies in coordinating the muscle movements necessary for speech.
2. Can children be affected by Aphasia or Apraxia?
Yes, children can be affected by Apraxia, known as Childhood Apraxia of Speech (CAS). Aphasia in children is less common but can occur, typically due to brain injury or a neurological condition.
3. Are Aphasia and Apraxia curable?
While there may not be a complete ‘cure,’ many individuals with Aphasia or Apraxia can improve significantly with appropriate therapy and support. Recovery depends on various factors, including the severity of the disorder and the type of intervention provided.
4. How important is early intervention in the treatment of Aphasia and Apraxia?
Early intervention is crucial in the treatment of both Aphasia and Apraxia. It can lead to more effective management of the conditions and significantly improve communication abilities.
5. Can Aphasia and Apraxia co-occur in the same individual?
Yes, it’s possible for an individual to have both Aphasia and Apraxia, especially if they have experienced a brain injury or stroke that affects multiple areas of the brain involved in language and speech.
6. What are the common causes of Aphasia?
The most common causes of Aphasia include stroke, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative diseases. It is typically associated with damage to the language-processing areas of the brain.
7. What role does speech therapy play in managing Aphasia and Apraxia?
Speech therapy is a critical component in managing both Aphasia and Apraxia. It involves personalized strategies and exercises to improve language processing and speech coordination, enhancing communication abilities.
8. How can family and friends support someone with Aphasia or Apraxia?
Support from family and friends can be incredibly beneficial. This can include being patient in conversations, using clear and simple language, encouraging the use of therapy techniques at home, and providing emotional and practical support.
9. Are there technological aids available for individuals with Aphasia or Apraxia?
Yes, there are various technological aids and tools designed to assist individuals with Aphasia or Apraxia. These range from communication apps to speech-generating devices, which can greatly aid in everyday communication.
10. Where can I find more information and support for Aphasia and Apraxia?
For more information and support, visit Wellness Hub’s dedicated sections on Aphasia and Apraxia, where you can access resources, therapy options, and community support to navigate these conditions.
About the Author:
Anuradha Karanam
Speech-language pathologist (7+ years of experience)
Anuradha Karanam is a skilled speech-language pathologist with over 6 years of experience. Fluent in Tamil, Telugu, Hindi, and English, she specializes in parent counseling, speech sound disorders, fluency assessment, and speech-language evaluations. Anuradha excels at working with children with developmental disorders, offering creative and effective therapy programs. Currently, at Wellness Hub, she holds a BASLP degree and is registered with the RCI (CRR No A85500). Her patience, ambition, and dedication make her a trusted expert in her field.
Connect with Anuradha to learn more about how she can help you or your loved one find their voice.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message







