Autism Levels Explained: A Practical Guide for Parents
By Wellness Hub
Last Updated: March 17, 2025
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) encompasses a wide range of conditions with varied challenges in social skills, repetitive behaviors, and communication. Understanding the different levels of autism is crucial as it helps tailor support and interventions to each individual’s unique needs. This guide aims to demystify these levels, providing you with insights to enhance care and education strategies effectively. Stay with us as we explore how a deeper understanding of ASD can empower those on the spectrum and their support networks.
Identify potential early signs of autism with our quick and reliable online screening. Start the Free Test
Overview of Autism Levels
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is not a one-size-fits-all diagnosis; it encompasses a variety of challenges and strengths that vary widely from one person to another. To better understand and support individuals with autism, experts use what’s commonly referred to as the “autism severity scale.” This scale helps categorize ASD into different levels based on the degree of support required by the individual.
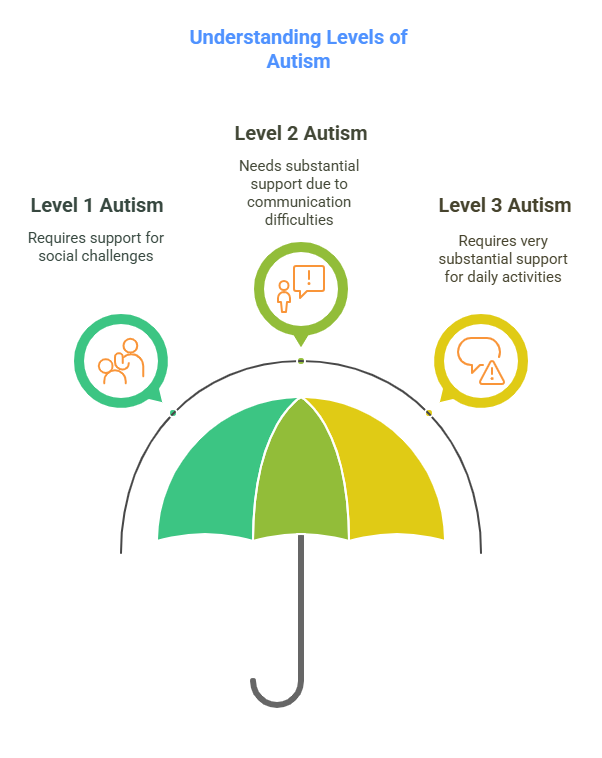
What are the Levels of Autism?
- Level 1: Requiring Support
- Individuals at this level may face difficulties in social situations, which could hinder their ability to function independently without support. They typically manage to speak and learn but struggle with organization and planning which can impact their daily functioning.
- Level 2: Requiring Substantial Support
- Those who fall into this category need more substantial support in their daily lives. They often exhibit marked deficits in verbal and nonverbal social communication skills, and social impairments are apparent even with supports in place. Their behaviors may limit or even disrupt their functioning in a variety of contexts.
- Level 3: Requiring Very Substantial Support
- Individuals at this level face severe challenges in communication and behaviors that prevent them from functioning independently. They require more intensive support and often have very limited ability to speak clearly or interact socially.
Also read: What is Autism? A Clear Guide for Parents and Caregivers
Detailed Explanation of Each Autism Level
Level 1 Autism
What does Level 1 autism mean?
Level 1 autism, often referred to as “high-functioning autism”, requires support primarily in social contexts. Individuals with Level 1 autism may find it challenging to initiate social interactions and may display atypical responses in social settings. They often manage daily tasks independently but may struggle with organization and planning which can affect their overall functionality.
Signs of Level 1 Autism in Adults:
- Difficulty in understanding social cues.
- Feelings of anxiety in social settings.
- Preference for routine and discomfort with unexpected changes.
Coping Strategies for Parents of Level 1 Autism:
- Establishing a predictable routine at home.
- Practicing social scenarios and appropriate responses.
- Encouraging independence while providing necessary support.
Level 2 Autism
Characteristics of Level 2 Autism
Level 2 autism requires substantial support. These individuals face more significant challenges in social interactions and exhibit restrictive and repetitive behaviors that are more pronounced and difficult to manage. Verbal and nonverbal communication often requires substantial support to be effective.
Behavioral Strategies for Level 2 Autism in Children:
- Use of visual aids to support communication.
- Structured behavioral interventions to manage repetitive behaviors.
- Consistent reinforcement of positive social interactions.
School Accommodations for Children with Level 2 ASD:
- Tailored learning environments with reduced distractions.
- Access to special education programs that cater specifically to their learning and developmental needs.
- Enhanced support from trained staff to facilitate social and educational integration.
Level 3 Autism
What Support Do Level 3 Autism Individuals Need?
Individuals with Level 3 autism require very substantial support, often due to severe challenges in verbal and nonverbal communication, as well as significant difficulties in understanding or maintaining social interactions. Their behaviors can be highly disruptive and are often self-stimulatory in nature.
Early Intervention for Level 3 Autism Spectrum Disorder:
- Intensive behavior therapy to develop basic communication skills.
- Early and consistent occupational therapy to assist in sensory integration.
- Focused interventions to develop and enhance social interaction skills.
Autism Level 3 Residential Support Options:
- Residential programs that provide 24-hour structured and therapeutic environments.
- Home-based setups that are heavily modified to ensure safety and consistency.
- Professional caregiving that supports daily living skills and behavior management.
Also read: Online Behavioral Therapy for Kids with Autism
Diagnostic Criteria and Assessment
When it comes to Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), understanding the criteria for diagnosis is crucial for professionals to accurately assess and support individuals. The process of determining where someone falls on the autism spectrum involves a thorough evaluation of their communication abilities, social skills, and behaviors.
Autism Classification and Diagnosis Criteria
The diagnostic criteria for ASD are detailed in standardized diagnostic manuals like the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition). These criteria include persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as well as restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.
Professionals look for symptoms that might have been present in the early developmental period, even if these symptoms become fully manifest only later. Importantly, these symptoms must cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of current functioning.
How Professionals Identify Your Child’s Autism Level
- Initial Screening:
- This usually involves a series of parent interviews and standardized screening tools to gather comprehensive information about the child’s behavior and development.
- Comprehensive Diagnostic Evaluation:
- This might include a detailed behavioral assessment, cognitive and language testing, and direct observation in different settings. Professionals such as developmental pediatricians, child psychologists, or neurologists are typically involved in this stage.
- Determining the Severity:
- Severity levels are assessed based on how much support an individual needs in social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors. The DSM-5 outlines three levels:
- Level 1: Requiring support
- Level 2: Requiring substantial support
- Level 3: Requiring very substantial support
- Severity levels are assessed based on how much support an individual needs in social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors. The DSM-5 outlines three levels:
Treatment and Support for Each Autism Level
Navigating the various treatment options for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can seem daunting. However, understanding the specific needs associated with each level of ASD severity can help in selecting the most effective therapies. Each level of autism presents unique challenges, and the treatment approach should be tailored accordingly to ensure optimal support and development.
Autism Spectrum Disorder Levels and Therapy Options
- Level 1 Autism: Requiring Support
- Main Focus: Social skills training and behavioral therapy to enhance communication and reduce social anxiety.
- Therapies Used:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to address anxiety and help manage responses to social situations.
- Social skills groups to provide practical training and peer interaction.
- Level 2 Autism: Requiring Substantial Support
- Main Focus: Intensive behavioral interventions and support in educational settings to manage more pronounced symptoms.
- Therapies Used:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) to reinforce positive behaviors and reduce unwanted actions.
- Speech therapy to improve communication skills, both verbal and non-verbal.
- Occupational therapy to assist with sensory integration and daily living skills.
- Level 3 Autism: Requiring Very Substantial Support
- Main Focus: Highly structured and specialized interventions to support severe communication and behavioral challenges.
- Therapies Used:
- Intensive, personalized behavioral plans focusing on basic communication skills and safety.
- Multi-disciplinary approach involving speech, occupational, and physical therapy to address a wide range of developmental needs.
- Residential care or day programs that provide structured environments tailored to individual needs.
Living with Autism: Challenges and Opportunities
Living with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities at every level of the spectrum. By understanding the autism scale and how autism levels are explained, individuals, families, and caregivers can better navigate the complexities of the condition, finding ways to turn challenges into opportunities for growth and fulfillment.
Autism Scale: Understanding the Impact on Daily Life
Each level of autism brings its own challenges, from social interaction difficulties to more significant behavioral needs. However, these challenges are accompanied by opportunities to harness unique talents and interests that many individuals with autism possess.
- Employment Opportunities for Adults with Level 3 Autism
- Challenges: Finding employment can be difficult due to limited social skills and higher needs for support.
- Opportunities: Programs tailored to neurodiversity are increasing, offering specialized job training and placement that focus on individual strengths, such as attention to detail and consistency in tasks.
- Transition Planning for Teens with Autism Spectrum Disorders
- Challenges: Moving from adolescence to adulthood involves significant changes in education, care, and lifestyle, which can be overwhelming for someone on the autism spectrum.
- Opportunities: Transition programs can help bridge this gap, providing teens with the skills needed for higher education, employment, and independent living. Schools and therapy centers, like those supported by Wellness Hub, often offer transition planning services that prepare teens for the next steps in their lives.
Embracing Neurodiversity and Effective ASD Communication Techniques
The concept of neurodiversity highlights the importance of recognizing and respecting neurological differences. By embracing this approach, society can help integrate individuals with autism more fully into community, work, and social settings.
ASD Communication Techniques:
- Visual Supports: Using visual schedules and prompts to aid understanding and reduce anxiety.
- Technology Aids: Employing apps and software designed to enhance communication for non-verbal individuals or those who struggle with traditional speech.
- Structured Environments: Creating predictable environments where individuals with autism can thrive by understanding what to expect and how to act.
Conclusion
Understanding different autism levels helps us better support those on the spectrum. It’s crucial to keep learning and adapting, as each person with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is unique. For more insights and tips, check out our engaging Wellness Hub resources. Dive into easy-to-understand articles, watch informative videos, and explore helpful infographics. Together, let’s enhance our knowledge and make a positive impact in the lives of individuals with autism. Join us at Wellness Hub and be part of a supportive community that grows and learns together!
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder is a range of conditions characterized by challenges with social skills, repetitive behaviors, and speech and nonverbal communication.
2. What are the different levels of autism?
There are three levels of autism, categorized based on the amount of support needed: Level 1 requires support, Level 2 requires substantial support, and Level 3 requires very substantial support.
3. How is autism diagnosed?
Autism is diagnosed through a combination of behavioral observations, developmental history assessments, and in some cases, medical testing, usually conducted by a team of healthcare professionals.
4. What signs of autism should parents look out for in children?
Signs to watch for include little or no eye contact, limited interest in peer relationships, delayed speech development, and repetitive behaviors or speech.
5. How can parents support a child with Level 1 autism?
Parents can support their child by providing structured routines, helping them develop social skills through practice, and seeking therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to manage anxiety.
6. What educational accommodations help children with Level 2 autism?
Children with Level 2 autism may benefit from individualized education programs (IEPs), visual aids, and access to special education services that cater to their specific learning needs.
7. Are there residential programs for individuals with Level 3 autism?
Yes, there are specialized residential programs that provide 24-hour structured and therapeutic environments tailored to meet the needs of those with Level 3 autism.
8. What therapies are effective for different levels of autism?
Effective therapies vary by autism level, including Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) for all levels, speech and occupational therapies for Level 2, and more intensive behavioral interventions for Level 3.
9. How can parents help their teens with autism transition to adulthood?
Parents can help by engaging in transition planning services that focus on developing skills necessary for independence, higher education, and employment.
10. Where can parents find more resources about autism?
Parents can visit Wellness Hub for a comprehensive range of resources, including articles, videos, and infographics, to learn more about autism and how to support their child effectively.
About the Author:
Shilpa Deshpande
Shilpa Deshpande is a skilled speech-language pathologist with over 14 years of experience. Fluent in Kannada, Telugu, Hindi, and English, she specializes in parent counseling, speech sound disorders, fluency assessment, and speech-language evaluations. Shilpa excels at working with children with developmental disorders, offering creative and effective therapy programs. Currently, at Wellness Hub, she holds a BASLP degree and is registered with the RCI. Her patience, ambition, and dedication make her a trusted expert in her field.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message









