Behavioral Therapy for Kids: What Every Parent Should Know
Last Updated: July 16, 2024
Parenting is both rewarding and challenging, filled with memorable milestones and inevitable struggles. When children face behavioral issues like tantrums, defiance, or anxiety, parents often feel overwhelmed. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial, and behavioral therapy offers a supportive path forward. This therapy helps children improve behaviors and emotional well-being through positive reinforcement and targeted strategies. It’s about more than just managing difficult behaviors; it’s about nurturing a happier, healthier childhood. Join us as we explore how behavioral therapy can make a difference in your child’s life.
What is Behavioral Therapy?
Behavioral therapy is a type of treatment that focuses on changing specific behaviors through various techniques and strategies. The core idea behind behavioral therapy is that all behaviors are learned and, therefore, can be unlearned or modified. This type of therapy is rooted in the principles of behaviorism, a theory that suggests that our actions are largely shaped by our interactions with the environment.

The primary goal of behavioral therapy is to replace undesirable behaviors with more positive ones. This is achieved through a range of methods, including positive reinforcement, time-outs, and modeling. Unlike other forms of therapy that delve into a person’s past to understand underlying issues, behavioral therapy is action-oriented and focuses on the present.
Also read: Online Behavioral Therapy for Kids
For parents, understanding these principles can be incredibly helpful. By using behavioral techniques, you can guide your child towards better behavior and improved emotional well-being. For example, rewarding your child for completing their homework on time can encourage them to continue this positive behavior.
The principles of behavioral therapy include:
- Positive Reinforcement: Rewarding desired behaviors to increase their occurrence.
- Punishment: Using consequences to reduce undesirable behaviors.
- Modeling: Demonstrating desired behaviors for children to imitate.
- Extinction: Removing reinforcement for unwanted behaviors to reduce their occurrence.
Why Consider Behavioral Therapy for Your Child?
Parenting comes with unique challenges, especially when your child has behavioral issues. These issues can range from mild concerns to serious conditions that impact daily life. Understanding and addressing these behaviors early can make a big difference in your child’s development and overall well-being.
Overview of Common Behavioral Issues in Children
Children can have a variety of behavioral problems, each with its own challenges. Here are some common issues:
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, ADHD can affect a child’s ability to focus and complete tasks.
- Anxiety Disorders: These include generalized anxiety disorder, separation anxiety, and specific phobias. Children with anxiety disorders often worry excessively and feel fearful.
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD): Marked by defiant and hostile behavior towards authority figures, children with ODD frequently argue and refuse to follow rules.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Children with ASD may have difficulties with social interactions, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
- Learning Disabilities: These can affect a child’s ability to learn and use academic skills, impacting their school performance.
- Depression: Symptoms include persistent sadness, irritability, and a loss of interest in activities.
Benefits of Early Intervention with Behavioral Therapy
Early intervention is crucial for addressing behavioral issues. Behavioral therapy offers many benefits that can help set your child on a successful path:
- Improved Behavior: Behavioral therapy focuses on positive reinforcement and other strategies to reduce undesirable behaviors and encourage positive ones.
- Enhanced Social Skills: Therapy can teach children how to interact more effectively with peers and adults, improving their social interactions.
- Better Emotional Regulation: Techniques learned in therapy can help children manage their emotions, reducing instances of anger, anxiety, and frustration.
- Increased Academic Performance: Addressing behavioral issues can lead to better focus and participation in school, enhancing academic achievement.
- Strengthened Parent-Child Relationships: Therapy often involves parents, helping to improve communication and understanding within the family.
Also read: Online Behavioral Therapy for Kids with Autism
Types of Behavioral Therapy
When it comes to helping your child manage their behavior, understanding the different types of behavioral therapy can be incredibly useful. Each type has its unique approach and benefits, making it possible to tailor the therapy to your child’s specific needs. Here are some of the most commonly used types of behavioral therapy:
1. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a highly structured approach that focuses on improving specific behaviors such as social skills, communication, and academics. It uses techniques like positive reinforcement to encourage desired behaviors and reduce undesirable ones. ABA is particularly effective for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) combines behavioral techniques with cognitive therapy to address the thoughts and feelings that influence behaviors. It helps children understand the connection between their thoughts, emotions, and actions. CBT is effective for treating a wide range of issues, including anxiety, depression, and ADHD.
3. Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT)
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) is a form of CBT that focuses on teaching children skills to manage their emotions, cope with stress, and improve relationships. It is especially useful for children who have intense emotional responses and struggle with interpersonal relationships. DBT combines individual therapy with group skills training sessions.
4. Exposure Therapy
Exposure Therapy is designed to help children overcome their fears and anxieties by gradually exposing them to the source of their fear in a controlled environment. This approach helps them build confidence and learn how to manage their anxiety. Exposure Therapy is often used to treat phobias, PTSD, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
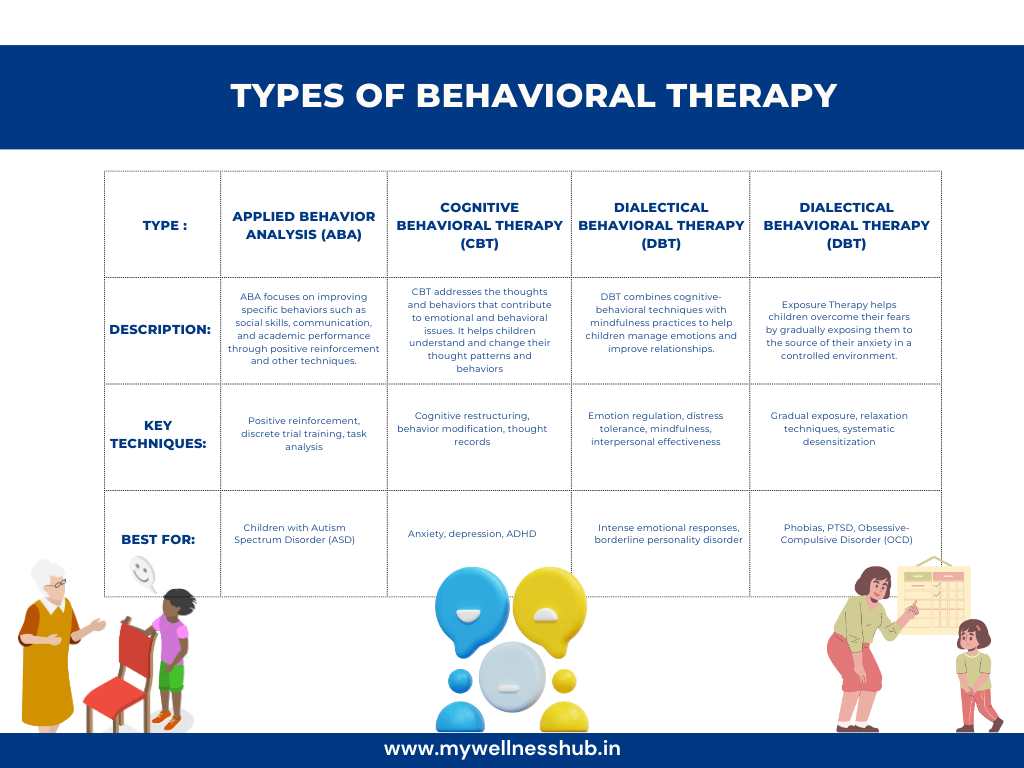
Comparison of Behavioral Therapy Types
| Therapy Type | Focus Area | Key Techniques | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) | Specific behaviors (social skills, communication) | Positive reinforcement, discrete trial training, task analysis | Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) |
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Thoughts and behaviors | Cognitive restructuring, behavior modification, thought records | Anxiety, depression, ADHD |
| Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) | Emotion management | Emotion regulation, distress tolerance, mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness | Intense emotional responses, borderline personality disorder |
| Exposure Therapy | Overcoming fears | Gradual exposure, relaxation techniques, systematic desensitization | Phobias, PTSD, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) |
Common Techniques Used in Behavioral Therapy
Understanding and using various behavioral therapy techniques can make a significant difference in managing your child’s behavior. Here are some effective techniques commonly used in behavioral therapy:
Positive Reinforcement Positive reinforcement involves rewarding your child for displaying desirable behaviors. This technique helps increase the likelihood that these behaviors will continue.
Examples:
- Praising your child for completing their homework.
- Offering a small treat for good behavior during a difficult task.
- Using a reward chart to track and reward progress.
Time-Outs
Time-outs can be an effective way to give your child a break and help them calm down. It’s important to use this technique correctly to ensure it is effective.
Dos and Don’ts:
- Do: Choose a quiet, distraction-free spot for the time-out.
- Do: Keep the duration short (one minute per year of age).
- Don’t: Use time-outs as a threat or punishment.
- Don’t: Engage in arguments or power struggles during the time-out.
Ignoring Negative Attention
Ignoring negative attention-seeking behaviors can reduce their frequency. This means not giving in to tantrums or other disruptive behaviors.
Key Points and Strategies:
- Remain calm and avoid eye contact or verbal responses during the behavior.
- Reinforce positive behaviors with attention and praise.
- After the behavior stops, calmly discuss better ways to express needs.
Effective Communication
Good communication is crucial for understanding and addressing your child’s needs. Using clear and positive communication techniques can improve your relationship and reduce conflicts.
Communication Power Tools:
- Eye Contact: Make eye contact to show you are listening.
- Active Listening: Listen without interrupting and acknowledge your child’s feelings.
- “I” Statements: Use statements like, “I feel upset when you don’t listen” to express your feelings without blaming your child.
- Clear Instructions: Give clear and concise instructions to avoid misunderstandings.
Modeling and Social Skills
Children learn a lot by observing others. Modeling appropriate behaviors and social skills can teach your child how to interact with others effectively.
Nurturing Social Skills:
- Demonstrate empathy, sharing, and problem-solving in your own actions.
- Role-play different social scenarios with your child.
- Encourage and praise your child when they display good social skills.
Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques can help your child manage stress and anxiety. These techniques can be integrated into daily routines to promote calmness.
Techniques and Benefits:
- Deep Breathing: Teach your child to take slow, deep breaths to calm down.
- Mindfulness: Practice mindfulness exercises like body scans or guided visualizations.
- Soothing Activities: Include calming activities like reading a book or listening to soft music before bedtime.
Creating a Positive Environment
A structured and positive home environment supports your child’s development and reduces behavioral issues.
Building a Supportive Home Environment:
- Establish predictable routines for meals, homework, and bedtime.
- Set clear and consistent rules and expectations.
- Create a clutter-free and calm home environment.
- Celebrate successes and milestones to foster a sense of accomplishment.
Chaining
Chaining involves breaking down a task into smaller steps and teaching each step individually. This technique is useful for teaching complex behaviors.
Explanation and Practical Uses:
- Forward Chaining: Start teaching the first step and gradually add subsequent steps.
- Backward Chaining: Teach the last step first and then work backward to the first step.
- Use chaining to teach tasks like dressing, brushing teeth, or completing a homework assignment.
Shaping
Shaping involves reinforcing successive approximations of a desired behavior. It helps children gradually learn new behaviors.
Explanation and Practical Uses:
- Identify the target behavior and reinforce small steps toward that behavior.
- Gradually increase the expectations as your child makes progress.
- Use shaping to teach skills like speaking in full sentences or completing chores.
Discrete Trial Training (DTT)
DTT is a structured teaching method that uses clear instructions and rewards. It is particularly effective for children with autism.
Explanation and Practical Uses:
- Break skills down into small, teachable components.
- Use a step-by-step approach with clear instructions and immediate reinforcement.
- Implement DTT to teach skills like recognizing colors, following instructions, or social interactions.
Common Behavioral Therapy Techniques
| Technique | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Reinforcement | Rewarding desired behaviors | Giving stickers for completed homework |
| Time-Outs | Short breaks to calm down | Using a quiet spot for time-outs |
| Ignoring Negative Attention | Not reinforcing unwanted behaviors | Avoiding eye contact during tantrums |
| Effective Communication | Using clear and positive communication | Making eye contact, using “I” statements |
| Modeling and Social Skills | Demonstrating desired behaviors | Role-playing social scenarios |
| Relaxation Techniques | Teaching stress management | Deep breathing exercises, mindfulness |
| Chaining | Breaking tasks into smaller steps | Teaching dressing by breaking it into steps |
| Shaping | Reinforcing successive approximations | Rewarding progress toward speaking in full sentences |
| Discrete Trial Training (DTT) | Structured teaching method | Teaching colors or following instructions |
When to Seek Professional Help
While many behavioral issues can be managed at home with the techniques we’ve discussed, there are times when professional help is necessary. Knowing when to seek the assistance of a behavioral therapist can make a significant difference in your child’s development and well-being.
Signs that Professional Help is Needed
- Persistent Behavioral Issues: If your child’s behavioral problems persist despite your best efforts to address them, it may be time to consult a professional.
- Severe Emotional Distress: Signs of severe anxiety, depression, or other emotional issues that impact daily functioning should not be ignored.
- Impact on Daily Life: If your child’s behavior is significantly affecting their school performance, social interactions, or family life, seeking help is crucial.
- Aggressive or Harmful Behaviors: Any behavior that poses a risk to your child or others requires immediate professional intervention.
- Regression in Development: If your child shows a noticeable regression in developmental milestones, it’s important to understand and address the underlying causes.
Benefits of Consulting a Behavioral Therapist
- Expert Assessment: A behavioral therapist can provide a thorough assessment to identify the root causes of your child’s behavior.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Therapists can develop customized plans tailored to your child’s specific needs and challenges.
- Professional Support: Ongoing support from a therapist can help you navigate difficult situations and implement effective strategies.
- Skill Development: Therapists can teach your child essential skills for managing emotions, improving social interactions, and enhancing academic performance.
- Parental Guidance: Behavioral therapists often work closely with parents, offering guidance and support to improve family dynamics and communication.
Finding a Behavioral Therapist
Finding the right behavioral therapist for your child is crucial for effectively addressing behavioral issues. Here’s a simple guide to help you find a qualified therapist who can meet your child’s specific needs.
Research and Referrals
Start your search by conducting thorough research and seeking referrals. Here are some tips:
- Online Searches: Use search engines to find therapists in your area. For example, search “behavioral therapist in [Your City]” to get local results.
- Professional Directories: Websites like the American Psychological Association (APA) or local mental health organizations often have directories of qualified therapists.
- Referrals: Ask for recommendations from your child’s pediatrician, school counselor, or friends and family who have had similar experiences.
- Wellness Hub Resources: Visit Wellness Hub for more information and guidance on finding a therapist.
Credentials and Specializations
Once you have a list of potential therapists, verify their credentials and specializations. Here’s what to look for:
- Licensing: Ensure the therapist is licensed Rehabilitation Council Of India(RCI). Licensing typically ensures the therapist has met specific educational and professional standards.
- Specialization: Look for therapists who specialize in working with children and have experience with the specific issues your child is facing (e.g., ADHD, autism, anxiety).
- Training: Check if the therapist has additional training in specific behavioral therapy techniques like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), or Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT).
Initial Consultations
The initial consultation is a crucial step in determining if a therapist is the right fit for your child. Here’s why it’s important and what to expect:
- Purpose: The consultation allows you to meet the therapist, discuss your child’s needs, and understand their approach to treatment.
- Questions to Ask: Inquire about their experience, therapeutic techniques, and how they involve parents in the process.
- Comfort Level: Ensure that both you and your child feel comfortable with the therapist, as a good rapport is essential for effective therapy.
Assessment and Treatment Plan
After choosing a therapist, the next steps involve assessment and developing a treatment plan. Here’s what this process typically involves:
- Comprehensive Assessment: The therapist will conduct a thorough assessment to understand your child’s behavior, developmental history, and any underlying issues.
- Customized Treatment Plan: Based on the assessment, the therapist will create a tailored treatment plan that outlines specific goals and strategies for addressing your child’s needs.
- Parental Involvement: The therapist will likely involve you in the treatment process, providing guidance on how to support your child at home and integrate therapy techniques into daily routines.
- Regular Updates: Expect ongoing communication with the therapist to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as necessary.
Statistics and Success Rates
Behavioral therapy has proven to be highly effective in treating various behavioral and developmental issues in children, such as ADHD, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and learning disabilities. Here, we’ll explore some statistics and success rates to highlight the impact of behavioral therapy on children’s lives.
Success Rates of Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy, including techniques like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), has shown significant success in improving the lives of children with different conditions. Here are some key statistics:
- ADHD: Research indicates that about 70-80% of children with ADHD show improvement in their symptoms when undergoing behavioral therapy. These improvements include better attention, reduced impulsivity, and enhanced ability to follow instructions.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Studies have shown that ABA therapy can lead to substantial gains in IQ, language skills, and adaptive behaviors in children with ASD. Approximately 47% of children who receive early intensive behavioral intervention achieve normal intellectual functioning.
- Learning Disabilities: Behavioral therapy can help children with learning disabilities develop better coping strategies, improve their academic performance, and enhance their social skills. Success rates vary, but many children show marked improvement in reading, writing, and math skills after consistent therapy.
Improvement Statistics
Behavioral therapy not only addresses specific behavioral issues but also contributes to overall development and well-being. Here are some areas where children typically show improvement after undergoing therapy:
- Academic Performance: Behavioral therapy helps children develop better focus and organizational skills, leading to improved performance in school. Studies show that children who receive behavioral therapy often see a significant increase in their grades and academic achievements.
- Social Skills: Therapy techniques such as social skills training and modeling can help children interact more effectively with their peers. Many children demonstrate enhanced communication skills and better relationships with friends and family.
- Emotional Regulation: Behavioral therapy teaches children how to manage their emotions, leading to fewer outbursts and improved mood stability. This is particularly beneficial for children with anxiety or mood disorders.
Long-Term Benefits
The benefits of behavioral therapy extend beyond immediate improvements. Children who undergo therapy often continue to use the skills they learn well into adulthood, leading to better long-term outcomes. These benefits include:
- Better Coping Strategies: Children learn how to deal with stress and frustration more effectively, which helps them navigate challenges in later life.
- Increased Independence: By improving their social, academic, and emotional skills, children become more independent and capable of handling various aspects of their lives.
- Higher Quality of Life: Overall, children who receive behavioral therapy tend to have a higher quality of life, with better mental health and well-being.
Conclusion
Behavioral therapy is a key player in shaping a positive future for your child by enhancing their emotional and social skills. If your child struggles with behavioral issues, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. At Wellness Hub, we offer expert guidance, personalized treatment plans, and unwavering support to ensure your child excels in life. You’re not alone in this journey—help is just a step away. Visit us for more resources and to start making a lasting difference in your child’s life today. Together, we can unlock their full potential.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is behavioral therapy for parents?
Behavioral therapy for parents involves using specific techniques to help their children develop healthier behaviors. It focuses on reinforcing positive behaviors and reducing negative ones through methods like positive reinforcement, time-outs, and effective communication.
2. How can parents use behavioral therapy at home?
Parents can use behavioral therapy at home by implementing techniques such as positive reinforcement, time-outs, ignoring negative attention-seeking behaviors, and modeling good behavior. These methods help children learn and practice desirable behaviors in a supportive environment.
3. Why is behavioral therapy important for children?
Behavioral therapy is important for children because it helps them develop better behavior, improve social skills, manage emotions, and perform better academically. Early intervention can lead to long-term positive outcomes in a child’s life.
4. How does behavioral therapy benefit parents and children?
Behavioral therapy benefits parents and children by improving communication, reducing conflicts, and fostering a positive home environment. It helps children develop coping strategies and better emotional regulation, leading to a more harmonious family life.
5. What are the basics of behavioral therapy for parents?
The basics of behavioral therapy for parents include understanding various techniques such as positive reinforcement, time-outs, modeling, and effective communication. These strategies help parents guide their children towards healthier behaviors and emotional well-being.
6. When should parents seek professional help for their child’s behavior?
Parents should seek professional help if their child’s behavioral problems persist despite using various techniques, if the child shows severe emotional distress, or if the behavior significantly impacts daily life. Consulting a behavioral therapist can provide expert guidance and support.
7. What are the success rates of behavioral therapy for conditions like ADHD and ASD?
Behavioral therapy has high success rates for conditions like ADHD and ASD. For example, about 70-80% of children with ADHD show improvement in symptoms, while children with ASD often experience significant gains in IQ, language skills, and adaptive behaviors with ABA therapy.
8. How do I find a qualified behavioral therapist for my child?
To find a qualified behavioral therapist, start by researching and seeking referrals from pediatricians, school counselors, or trusted friends. Verify the therapist’s credentials, specialization, and experience with children. Initial consultations are important to ensure a good fit for your child’s needs.
9. What are some common techniques used in behavioral therapy?
Common techniques used in behavioral therapy include positive reinforcement, time-outs, ignoring negative attention, effective communication, modeling and social skills training, relaxation techniques, chaining, shaping, and discrete trial training (DTT).
10. Can behavioral therapy improve my child’s academic performance?
Yes, behavioral therapy can improve a child’s academic performance by enhancing focus, organizational skills, and emotional regulation. Techniques like positive reinforcement and effective communication help children develop better study habits and perform better in school.
About Author:
Lasya Vooturi
Clinical Psychologist and Behavioral Therapist
Lasya holds a Professional Diploma in Clinical Psychology from Amity University, where she deepened her understanding of psychological principles from March 2023 to March 2024. With over a year of dedicated experience as a Behavioral Therapist, Lasya has honed her skills in applying effective therapy techniques tailored to individual needs. Fluent in Telugu, Hindi, and English, she is adept at connecting with a diverse range of clients, ensuring comprehensive communication and understanding. Lasya’s approach is grounded in empathy and scientific rigor, making her a trusted ally in navigating mental health challenges.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message








