Enhancing Kids Writing: Key Fine Motor Skills Development
By Rajini D
Last Updated: December 18, 2023
Introduction
In the intricate journey of childhood development, the acquisition of fine motor skills, is a crucial precursor to the art of writing. The pencil grasp, hand arching, in-hand manipulation, and thumb opposition are integral components of these skills. These lay the foundation for efficient and comfortable handwriting. This comprehensive article delves into the nuances of each skill, exploring their significance in pre-writing abilities. Moreover, it addresses the vital question: How can we identify problems in a child’s pre-writing skills? The important step is to understand the Key Fine Motor Skills.
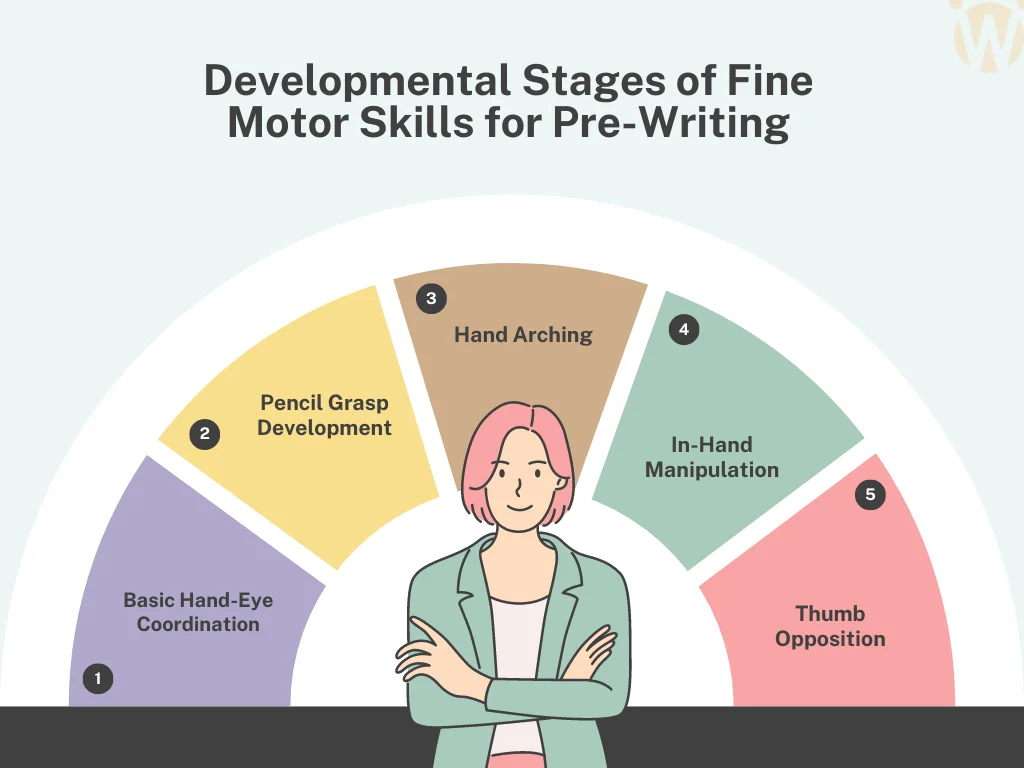
Pencil Grasp: The Dance of Precision
Pencil grasp refers to the way a child holds a pencil, and its significance extends beyond mere posture. A functional pencil grasp is characterized by efficiency, comfort, and an absence of fatigue. The dynamics of how a child holds a pencil influence their ability to form letters and words. There are various types of pencil grasps, from the dynamic tripod grasp to the lateral tripod grasp. These unveil the intricate dance of precision required for successful handwriting.
Know more about on Help Your Child Develop a Strong Pencil Grasp
Hand Arching: Shaping for Skilful Movement
Hand arching is the molding of hand arches for skillful finger movement. These arches play a pivotal role in creating the optimal conditions for control and dexterity during object manipulation. The proper shaping of hand arches ensures that a child can navigate the fine line between grip strength and flexibility. This facilitates the fluidity necessary for effective pre-writing skills.
In-hand Manipulation: Mastering the Solo Symphony
In-hand manipulation involves the art of moving and manipulating objects within one hand without the assistance of the other. This skill is a solo symphony, showcasing a child’s ability to rotate, shift, and adjust objects within their grasp. From turning a pencil to repositioning a small item, in-hand manipulation is the orchestration of fine motor control within the confines of a single hand.
Thumb Opposition: The Foundation of Precision
The ability of the thumb to touch the tips of the other fingers is known as thumb opposition. This seemingly simple action forms the foundation for holding and manipulating objects, such as a pencil, with precision. The opposition of the thumb enables a pincer grasp. Further, this would allow a child to pick up small items and engage in the intricate movements necessary for pre-writing tasks.
Identifying Problems in Pre-Writing Skills: A Diagnostic Journey
Recognizing challenges in a child’s pre-writing skills is a delicate task. It requires a keen understanding of the interplay between motor skills and the act of writing. Here are key indicators that may signal difficulties:
Awkward Pencil Grasp:
An unconventional or awkward pencil grasp, can be a fisted grip or fingers positioned too far from the pencil. This may indicate challenges in developing an efficient and comfortable grasp.
Inconsistency in Hand Arching:
Inconsistencies in shaping hand arches during fine motor tasks may suggest difficulties in achieving the necessary balance between control and flexibility. This can impact a child’s ability to manipulate writing instruments effectively.
Limited In-Hand Manipulation Skills:
Difficulty rotating, shifting, or adjusting objects within the hand may point to challenges in in-hand manipulation. This skill is crucial for tasks like adjusting the grip on a pencil or maneuvering paper during writing.
Weak Thumb Opposition:
A weak or absent thumb opposition, where the thumb struggles to touch the tips of the other fingers, can hinder a child’s ability to hold and manipulate writing tools with precision.
Poor Handwriting Control:
Ultimately, poor handwriting control itself can be a clear indicator of underlying issues in fine motor skills. Illegible or laboured writing may signal difficulties in pencil grasp, hand arching, in-hand manipulation, or thumb opposition.
Learn more: Effect of Handwriting on Underachievers and Tips to Improve it
Addressing Challenges: Intervention and Support
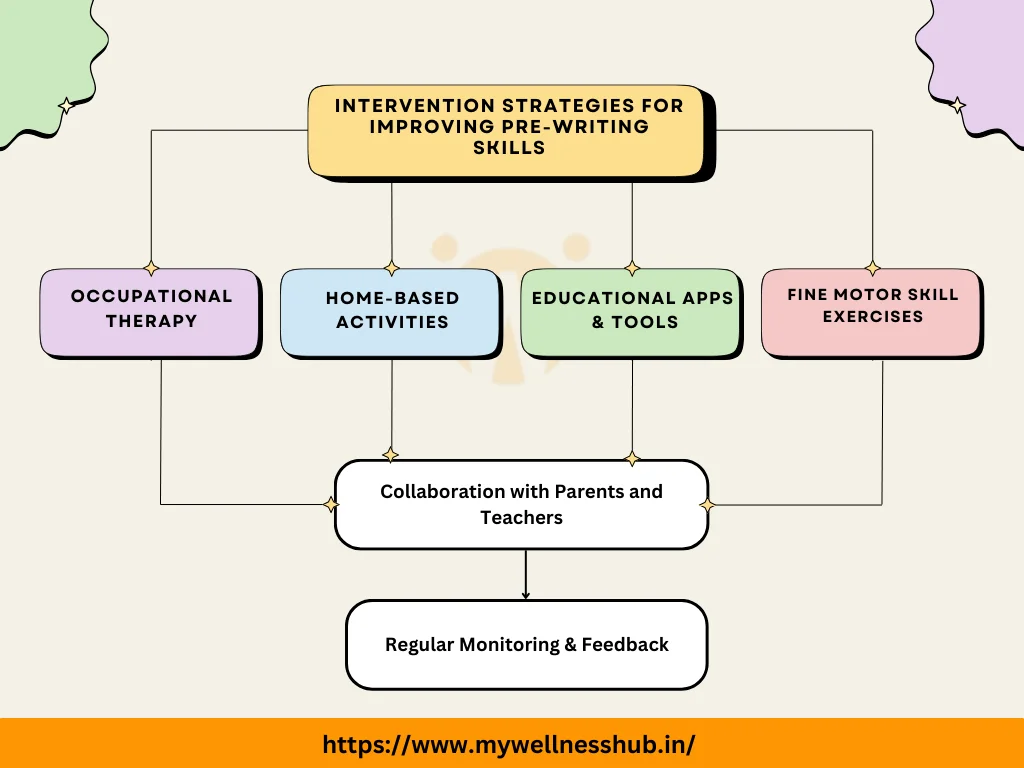
Once challenges in pre-writing skills are identified, appropriate intervention and support become imperative. This may involve targeted occupational therapy sessions, home-based activities, or collaborative efforts between educators and parents. Therapists may employ exercises to enhance pencil grasp, promote hand arching, refine in-hand manipulation, and strengthen thumb opposition.
Conclusion
In the journey towards proficient writing, the assessment of fine motor skills is a compass that guides us. The detailed intricacies would include pencil grasp, hand arching, in-hand manipulation, and thumb opposition. By understanding the significance of each skill and being vigilant for signs of difficulty, parents, educators, and therapists can collaboratively nurture a child’s pre-writing abilities. In fact, the art of writing begins with the finesse of motor control and in recognizing and addressing challenges. Through them, we can empower the next generation to script their stories with confidence and skill.
FAQs
1. What are the key fine motor skills involved in pre-writing abilities?
Fine motor skills crucial for pre-writing abilities include pencil grasp, hand arching, in-hand manipulation, and thumb opposition.
2. Why is pencil grasp important in childhood development?
Pencil grasp is vital because it affects a child’s ability to write efficiently and comfortably, influencing their ability to form letters and words.
3. What is hand arching, and how does it contribute to writing skills?
Hand arching is the molding of hand arches for skilled finger movement, essential for control and dexterity during object manipulation, impacting a child’s writing abilities.
4. What does in-hand manipulation entail, and why is it significant?
In-hand manipulation involves moving and manipulating objects with one hand, which is crucial for tasks like rotating a pencil or adjusting grip, thereby affecting writing precision.
5. How does thumb opposition affect a child’s writing ability?
Thumb opposition, the ability of the thumb to touch the tips of other fingers, is foundational for holding. It is also essential for manipulating objects like pencils, essential for precise writing movements.
6. What are the signs of problems in a child’s pre-writing skills?
Indicators of issues include awkward pencil grasp, inconsistency in hand arching, limited in-hand manipulation skills, weak thumb opposition, and poor handwriting control.
7. How can an unconventional pencil grasp affect a child’s writing?
An unconventional pencil grasp, like a fisted grip, can lead to inefficiency, discomfort, and fatigue. All these could hinder the child’s ability to write effectively.
8. What role does thumb opposition play in picking up small items?
Thumb opposition enables a pincer grasp, allowing a child to pick up small items. The child will be engaged in intricate movements necessary for writing and other fine motor tasks.
9. What interventions can help children with challenges in pre-writing skills?
Interventions may include occupational therapy, home-based activities, and collaborative efforts between educators and parents to enhance various fine motor skills.
10. How does poor handwriting control indicate underlying fine motor skill issues?
Illegible or laboured writing may signal difficulties in fine motor skills. The examples of fine motor skills can be like, pencil grasp, hand arching, in-hand manipulation, or thumb opposition. They require targeted intervention.
About the Author:
Rajini, Speech-Language Pathologist:
Rajini is a dedicated Speech-Language Pathologist with a focus on developmental speech and language disorders in children and rehabilitation in adults. With a passion for helping each individual find their voice, Rajini brings a wealth of experience and a heartfelt approach to therapy. At Wellness Hub, she’s part of a team that values innovation, compassion, and results-driven practices.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message








