Oral motor Exercises: Key to Better Speech
By Rajini D
Last Updated: November 23, 2023
Oral motor exercises, also known as orofacial exercises, stand as a valuable tool in the realm of speech therapy, occupational therapy, and physical therapy. These exercises target the muscles in the mouth and face, aiming to strengthen and improve their functioning. Widely used to enhance oral motor skills, oral motor exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals with speech and swallowing disorders, as well as those facing neurological damage or muscle weakness in the orofacial region. In this article, we delve into the significance of Oral motor exercises, explore various exercises targeting different muscle groups, and highlight the important benefits they offer, especially in the context of speech and language development.
Exploring Oral Motor exercises:
Oral motor exercises are activities that strengthen the muscles of the mouth and face, which are crucial for functions such as speaking, swallowing, and facial expression. These exercises can be particularly beneficial for children who have difficulties in these areas due to developmental delays, neurological disorders, or other health conditions. Here are some effective oral motor exercises for children:
Blowing Exercises:
- Blow Bubbles: Encourage the child to use a bubble wand to blow bubbles. This activity is fun and engaging, and it serves to strengthen the muscles required for breath control and lip rounding, which are crucial for clear speech production. The act of blowing creates resistance in the oral cavity, which enhances muscle tone and coordination.
- Blow Cotton Balls: Have the child blow a cotton ball across a table using a straw. This exercise targets precise control over breath and lip position, crucial for phonetic articulations and fluent speech. It’s also a playful way to develop sustained breath, which is necessary for longer sentences and speech clarity.
Swallowing Exercises:
Swallowing exercises help in managing the airflow control through the throat area and effective usage of throat muscles in coordinating the movement of food into the food pipe.
- Swallowing different textures of food: Introduce foods with various textures to practice adjusting the swallowing technique accordingly. This helps in managing sensory processing issues and prepares the child for a variety of dietary consistencies.
- Practicing specific swallowing patterns: Guide the child through targeted exercises that mimic different swallowing stages, improving the coordination of muscles in the throat and reducing the risk of choking.

Sucking and Straw Exercises:
- Sucking through a Straw: Use straws of different diameters to drink various liquids, from water to smoothies. This variation in texture and straw size helps strengthen the lips and cheeks, improving the child’s ability to manage different oral sensations and textures, which is beneficial for both speech and safe swallowing.
- Straw Pickup Game: This game involves using a straw to suck up and hold small paper pieces, enhancing the child’s sucking strength and coordination. It’s an excellent exercise for kids to improve their control over sucking mechanisms, which play a role in speech sounds involving pressure, like ‘p’ and ‘b’.
Tongue Exercises:
- Tongue Push-ups: Encourage the child to push their tongue against the roof of the mouth and hold it for a few seconds before releasing. Repeat this several times to strengthen the tongue, which is vital for articulating sounds correctly and for effective swallowing.
- Tongue Tracking: Have the child move their tongue to follow patterns traced on the outside of their cheeks. This improves tongue mobility and coordination, essential for forming different speech sounds and for manipulating food while chewing.
Also read: Oral Motor Exercises: Tongue Exercises for Confident Speech
Lip Exercises:
- Lip Presses: Instruct the child to press their lips together tightly and then release. Repeating this exercise helps build lip strength, which is necessary for sounds that require lip closure like ‘p’, ‘b’, and ‘m’, and also aids in preventing drooling.
- Funny Faces: Playing a game of making various facial expressions, such as wide smiles or puckered lips, can significantly improve facial muscle control and flexibility, adding to the expressive abilities of the child.
Know more: Oral Motor Exercises: Lip Exercises for Speech Development
Chewing Exercises:
- Chewy Foods: Provide chewy foods like gummies or bagels, which require more effort to chew. This activity helps develop jaw strength and endurance, essential for effective speech and eating solid foods.
- Textured Toys: Let the child chew on safe, textured toys or rubbery tubes. This not only helps in strengthening the jaw muscles but also stimulates the sensory receptors in the mouth, which are critical for sensory integration and speech clarity.
Learn more about our article on Top Activities for Biting and Chewing in Children
Facial Massage:
- Gently massage the child’s face with your fingertips. This can help increase awareness of facial muscles, reduce muscle tightness, and promote relaxation, making it easier for the child to engage in speech and facial expression activities.
Singing and Music:
- Engage the child in singing songs that involve making long sounds or exaggerated facial movements. This fun and interactive method helps with breath control and articulation, as well as rhythm and phonetic accuracy, which are fundamental aspects of fluent speech.
Read more: Benefits of Using Music and Songs to Boost Speech Articulation
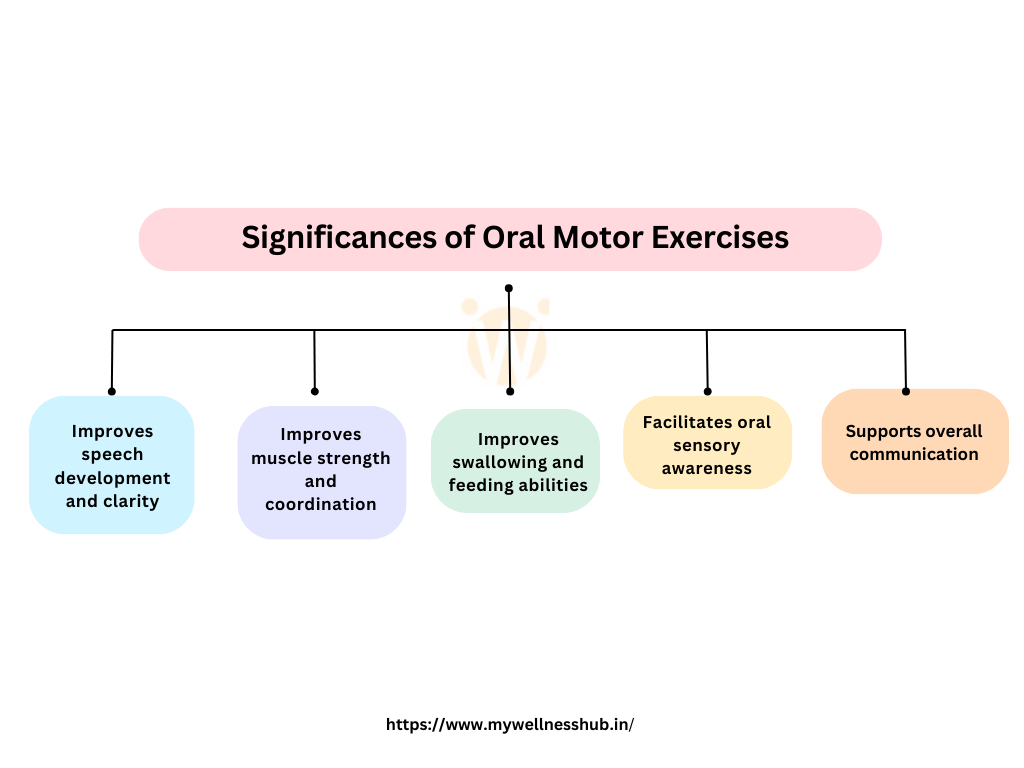
Important Benefits of Oral Motor Exercises:
Oromotor exercises play a pivotal role in speech and language development, offering a myriad of benefits for individuals facing speech and language disorders, difficulties, or neurological impairments affecting orofacial muscles. Here are some key benefits:

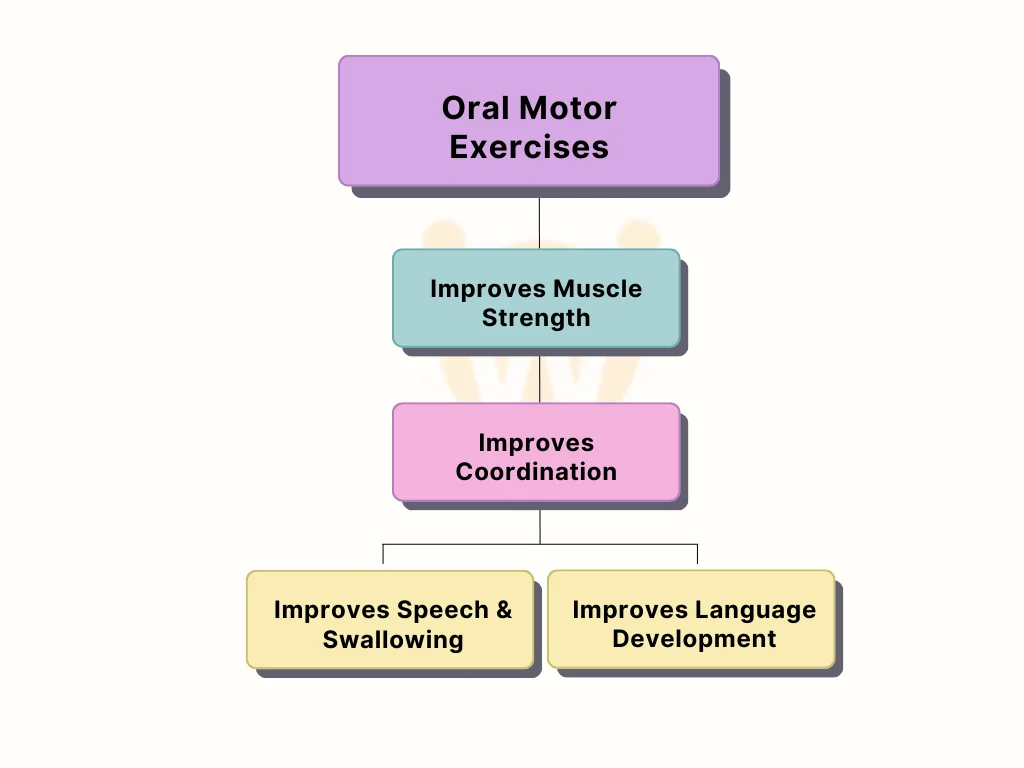
1. Improving Muscle Strength and Coordination:
Oral motor exercises are designed to systematically enhance the strength, flexibility, and coordination of the orofacial muscles—lips, tongue, jaw, and cheeks. This targeted strengthening is crucial for executing precise movements necessary for speech articulation. Stronger muscles lead to clearer and more distinct articulation, enabling more precise speech movements that are fundamental for producing a variety of sounds accurately.
2. Speech Improvement:
By targeting specific muscles involved in speech production, these exercises contribute directly to significant improvements in articulation, pronunciation, and the overall clarity of speech. This targeted approach allows for the correction of speech sound errors and enhances the fluency and expressiveness of communication, making it easier for individuals to convey their thoughts and emotions clearly and effectively.
Know more about our article on Top Speech Pathology Exercises for Better Communication
3. Facilitating Swallowing and Feeding Skills:
Oral motor exercises play a critical role in reinforcing the muscle groups involved in the complex process of swallowing, thereby aiding individuals who struggle with dysphagia or other swallowing disorders. By improving the coordination of these muscles, the exercises help ensure a safer, more efficient swallowing process which is essential for good nutrition and the enjoyment of a variety of foods, reducing the risk of choking or aspiration.
4. Promoting Oral Sensory Awareness:
These exercises also enhance oral sensory awareness, which is the ability to perceive and respond to different stimuli within the oral cavity. Improved sensory awareness aids individuals in better controlling their oral muscle movements during speech and feeding, which is particularly beneficial for those with sensory processing issues. Enhanced sensory feedback helps fine-tune motor responses, leading to improved precision in speech and safer eating habits.
5. Oral Motor Skills in Children:
For children experiencing speech and language development delays, oral motor exercises are instrumental in developing fundamental oral skills. These activities are tailored to improve the movement of the lips and tongue and enhance overall muscle tone, which are essential for forming sounds, words, and eventually fluent speech. Regular practice can accelerate the development of these essential skills, helping bridge the gap in speech and language proficiency.
6. Tongue Thrust Correction:
Tongue thrust refers to a condition where the tongue protrudes through the front teeth during speech or swallowing, which can lead to orthodontic issues or impaired speech clarity. Oral motor exercises are effectively used to retrain the tongue, teaching it to position correctly within the mouth, thus preventing the associated dental and speech problems. These exercises are designed to promote proper tongue placement and strengthen the tongue’s ability to maintain correct posture.
7. Enhancing Overall Communication Skills:
Improved oral motor function significantly enhances overall communication abilities. Strengthening the orofacial muscles not only boosts the mechanical skills needed for speech but also builds confidence in one’s ability to communicate. With better control and strength, individuals can speak more fluently, express themselves more clearly, and participate more fully in social interactions, thereby improving their quality of life.
Oral Motor Functioning in Various Aspects of Daily Life
- Articulation: This involves the ability to move the lips, tongue, and jaw to produce clear and distinct speech sounds. Proper articulation is crucial for spoken language.
- Chewing and Swallowing: Effective chewing and swallowing require the coordinated efforts of the jaw, tongue, and cheeks to manipulate and process food, preparing it to be safely swallowed.
- Breathing Control: Controlling the breath for speech involves the muscles around the mouth and respiratory system. It is essential for speech clarity and volume control.
- Facial Expression: The muscles of the face allow for the expression of emotions, such as happiness, sadness, or surprise, which are important for non-verbal communication.
- Lip Closure: The ability to close the lips completely is vital for functions such as sucking through a straw, blowing, and making certain speech sounds.
- Tongue Coordination: The tongue must be able to move precisely for different tasks, including articulating sounds, managing food while eating, and cleaning the teeth
- Improving Speech Clarity: By strengthening the muscles involved in articulation, oral-motor therapy can help enhance the clarity and quality of speech, making it easier for children and adults to communicate effectively.
- Reducing Drooling: Strengthening the muscles around the mouth can help control saliva and reduce drooling, which is especially important for hygiene and social interactions.
- Facilitating Better Oral Hygiene: Improved muscle control can help an individual manage oral hygiene tasks more effectively, like brushing teeth and using mouthwash.
Who needs oral-motor exercises?
- Children with Speech Delays: If a child is experiencing delays in developing clear speech, oral-motor exercises can help improve the strength and coordination of the muscles involved in speech production.
- Individuals with Neurological Disorders: People with neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, or traumatic brain injury might have impaired control of their mouth and facial muscles. Oral-motor exercises can help enhance their muscle function and speech clarity.
- Children with Developmental Disorders: Children diagnosed with developmental disorders like Down syndrome or autism spectrum disorders often benefit from these exercises, as they frequently face challenges with muscle tone and coordination.
- Those with Feeding and Swallowing Difficulties: Oral-motor exercises can assist individuals who have trouble with sucking, chewing, or swallowing. This can include young children who are transitioning from liquid to solid foods or older individuals recovering from medical conditions affecting their swallowing muscles.
- Individuals with Oral Apraxia: Oral apraxia is a condition where the person has difficulty executing voluntary movements for speech despite having no muscle paralysis or weakness. Exercise can help improve the planning and coordination of these movements.
- People Seeking to Improve Articulation for Acting or Singing: Actors, singers, and other performers sometimes use oral-motor exercises to enhance their articulation and control over their voice and facial expressions.
How and when should you practice with your child?
How to Practice Oral-Motor Exercises
- Make It Fun: Keep the sessions light and enjoyable. Use games, songs, and playful activities to engage your child. This can make it easier for them to participate and can help keep their interest alive.
- Incorporate Variety: Change up the exercises and activities to prevent boredom. This can also help target different muscle groups and skills.
- Use Visuals and Demonstrations: Children often learn better through visual cues and mimicry. Show them how to do the exercises by doing them yourself. You can also use mirrors so they can see themselves.
- Give Clear Instructions: Use simple, concise language to explain what you want them to do. Break the exercises into small, manageable steps.
- Provide Positive Feedback: Encourage your child with positive reinforcement. Celebrate their efforts and improvements, no matter how small.
When to Practice Oral-Motor Exercises
- Regular Short Sessions: Short, frequent practice sessions are more effective than long, infrequent ones. Aim for a few minutes at a time, several times a day. Consistency is key.
- Best Times of Day: Choose times when your child is most alert and responsive. This might be in the morning after breakfast or in the afternoon after a nap. Avoid times when they are tired or hungry.
- Integrate with Daily Activities: Incorporate exercises into daily routines. For example, practice lip rounding while brushing teeth or do tongue movements during story time.
- Before Meals: Doing exercises before meals can be particularly effective as it helps prepare the muscles for eating and can make feeding easier.
- As Part of Speech Therapy: If your child is attending speech therapy, coordinate with their therapist to align the home exercises with their therapy goals. This ensures consistency and reinforces what they learn during therapy sessions.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Practices
- Observe and Adapt: Monitor your child’s progress and adjust the exercises accordingly. If an exercise seems too difficult, simplify it, or if it becomes too easy, make it more challenging.
- Seek Professional Advice: Regular check-ins with a speech-language pathologist or occupational therapist can help you stay on track, make necessary adjustments, and get professional feedback on your child’s progress.
Why are these exercises and Speech therapy important?
Speech and language development is a critical aspect of a child’s overall growth, influencing their ability to communicate effectively and engage with the world. For some children, speech-related challenges may arise, impacting their articulation, language skills, and overall communication abilities. In such cases, speech therapy and targeted exercises at home can play a pivotal role in fostering improvement.
Speech and language development in children is a dynamic process that involves the acquisition and mastery of communication skills. From the early babbling of infants to the complex language structures of older children, each stage is crucial for building a strong foundation. However, some children may encounter difficulties along the way, leading to speech issues that can impact their daily lives and interactions.
Speech therapy emerges as a valuable intervention for children experiencing speech-related challenges. Speech therapists, also known as speech-language pathologists (SLPs), specialize in assessing and treating speech and language disorders. They work collaboratively with children and their families to identify specific challenges and develop targeted strategies for improvement.
Conclusion
Oral motor exercises are essential for enhancing speech and eating skills. At Wellness Hub, we advocate for these simple yet effective techniques that strengthen mouth muscles, helping everyone from young children facing developmental delays to adults recovering from strokes. Regular practice can significantly improve speech clarity and eating ease. Discover more engaging exercises by visiting our comprehensive speech therapy guide. With consistent effort, you’ll see remarkable improvements. Consult with our expert speech therapists at Wellness Hub for personalized exercise plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are oral motor exercises, and how do they contribute to speech and swallowing improvement?
Oral motor exercises, also known as orofacial exercises, target muscles in the mouth and face to enhance strength and coordination. They play a crucial role in speech therapy, benefiting individuals with speech and swallowing disorders, as well as those with orofacial muscle weaknesses.
2. Can you provide examples of oral motor exercises targeting different muscle groups?
Certainly, Examples include lip exercises (puckering, smiling widely), tongue exercises (moving the tongue, touching it to different parts of the mouth), jaw exercises (opening and closing, moving side to side), cheek exercises (inflating and releasing), and swallowing exercises (practicing different food textures, specific swallowing patterns).
3. What are the key benefits of oral motor exercises for speech and language development?
Oral motor exercises offer benefits such as improved muscle strength and coordination, enhanced speech production, better swallowing and feeding skills, increased oral sensory awareness, and correction of issues like tongue thrust. They are particularly valuable for children with speech and language delays.
4. Why is it important for oral motor exercises to be guided by healthcare professionals?
Trained professionals, including speech-language pathologists, occupational therapists, or dentists, ensure that oral motor exercises are tailored to individual needs and goals. Their expertise is crucial in providing a comprehensive assessment and targeted treatment plan.
5. How do oral motor exercises contribute to communication skills and confidence?
Improved oral motor function improves communication skills by strengthening speech production muscles, boosting confidence, and enhancing fluency. This empowerment allows individuals to express thoughts and ideas more clearly and effectively.
6. Can oral motor exercises help with drooling issues?
Yes, oral motor exercises can help reduce drooling by strengthening the lip and cheek muscles, improving the ability to close the mouth fully, and enhancing the control over saliva.
7. What signs might indicate a need for oral motor exercises?
Signs that might indicate the need for oral motor exercises include difficulties with chewing or swallowing, unclear speech, excessive drooling, and challenges with any activity that involves the lips, jaw, tongue, or cheeks.
8. Can oral motor exercises be fun for children?
Absolutely! Many oral motor exercises can be turned into fun activities, such as blowing bubbles, playing with whistles, and making funny faces. Incorporating games and playful elements can make these exercises more enjoyable and engaging for children.
9. How do oral motor exercises impact speech therapy?
Oral motor exercises are a crucial part of speech therapy that complement other therapeutic approaches. They directly improve the physical capabilities necessary for speech, enhancing the effectiveness of speech therapy outcomes.
10. Are there any risks associated with oral motor exercises?
Oral motor exercises are generally safe when performed correctly. However, it’s important to use appropriate tools and follow instructions from a qualified speech-language pathologist to avoid potential issues, such as jaw strain or inappropriate swallowing techniques.
About the Author:
Rajini Darugupally
M.Sc., Speech-Language Pathologist (9+ years of experience)
Rajini is a passionate and dedicated Speech-Language Pathologist with over 9+ years of experience, specializing in both developmental speech and language disorders in children and rehabilitation in adults. Driven by a desire to empower each individual to find their voice, Rajini brings a wealth of experience and a warm, genuine approach to therapy. Currently, at Wellness Hub, she thrives in a team environment that values innovation, compassion, and achieving results for their clients.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message








