Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Simple Parent Guide
By Wellness Hub
Last Updated: August 27, 2024
In a world that moves at breakneck speed, mental health has emerged as a cornerstone of maintaining overall well-being. Amidst our bustling lives, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, or CBT, stands out as a beacon of hope for many grappling with psychological issues. CBT is a form of psychotherapy that is lauded for its effectiveness in addressing a wide array of psychological problems—from deep-seated depression and anxiety to stress resulting from daily challenges.
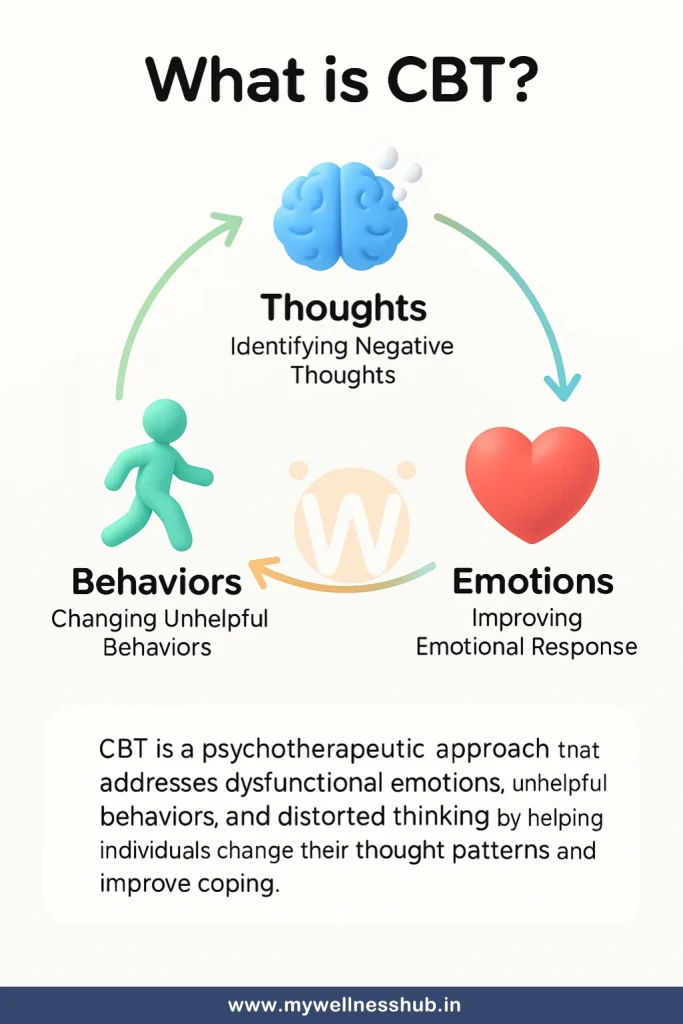
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is more than just a method of treatment—it’s a transformative approach to mental healthcare that emphasizes the interconnectivity of thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. CBT operates on the fundamental belief that our thoughts and interpretations of events influence our feelings and actions. Therefore, by changing destructive thoughts, we can change our emotions and behaviors, leading to improved mental health and well-being.
Unlike traditional psychotherapies that may delve deep into one’s past experiences, CBT is distinctly structured and goal-oriented. Each session is designed to be both directive and problem-solving in nature, focusing specifically on the issues that are most distressing to the individual at that time. This makes CBT exceptionally efficient; it typically involves fewer sessions than other forms of therapy and focuses on equipping individuals with practical skills to manage specific problems.
Also read: Online Behavioral Therapy for Kids
Core Principles of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
At the heart of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) are two foundational beliefs that shape its unique approach to addressing psychological issues. First, CBT posits that psychological problems are significantly influenced by unhelpful and often inaccurate thoughts. Second, it acknowledges that many of these problems stem from learned patterns of unhelpful behavior. Together, these principles form the basis of CBT’s highly effective treatment strategies.
1. The Impact of Unhelpful Thinking
Many of us harbor destructive thought patterns—whether it’s a tendency to catastrophize, overgeneralize, or engage in black-and-white thinking. These patterns not only distort our perception of reality but also adversely affect our emotional and mental well-being. CBT tackles these issues head-on by helping individuals recognize and challenge these unhelpful thoughts. The goal is to replace them with more balanced and realistic thoughts, which can lead to healthier emotions and more constructive behaviors.
2. Breaking the Cycle of Maladaptive Behaviors
Behavioral patterns, such as avoidance or withdrawal, often develop as responses to distressing thoughts and emotions. However, while these behaviors might provide temporary relief, they can lead to more significant issues in the long run. CBT helps individuals break these cycles by introducing healthier behavioral strategies. Through techniques like exposure therapy, role-playing, or gradual step-by-step accomplishment of tasks, individuals learn to face rather than avoid their challenges.
3. How CBT Modifies Thoughts and Behaviors
CBT is not about simply ‘thinking positively’; it’s about fostering a realistic and objective way to view and interact with the world. Therapists guide clients through a structured process to identify specific problems and set realistic goals. Clients learn to apply various techniques to manage and change their thoughts and behaviors actively. This process often involves homework assignments—practical tasks that reinforce the lessons learned during therapy sessions, ensuring continuous progress.
4. Empowerment Through Self-Awareness
One of the most empowering aspects of CBT is its focus on equipping individuals with the tools they need to become their own therapists. By internalizing CBT techniques, clients can not only address current issues but also apply these skills to future challenges, promoting long-term mental health resilience.
Also read: Online Behavioral Therapy for Kids with Autism
The Process of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
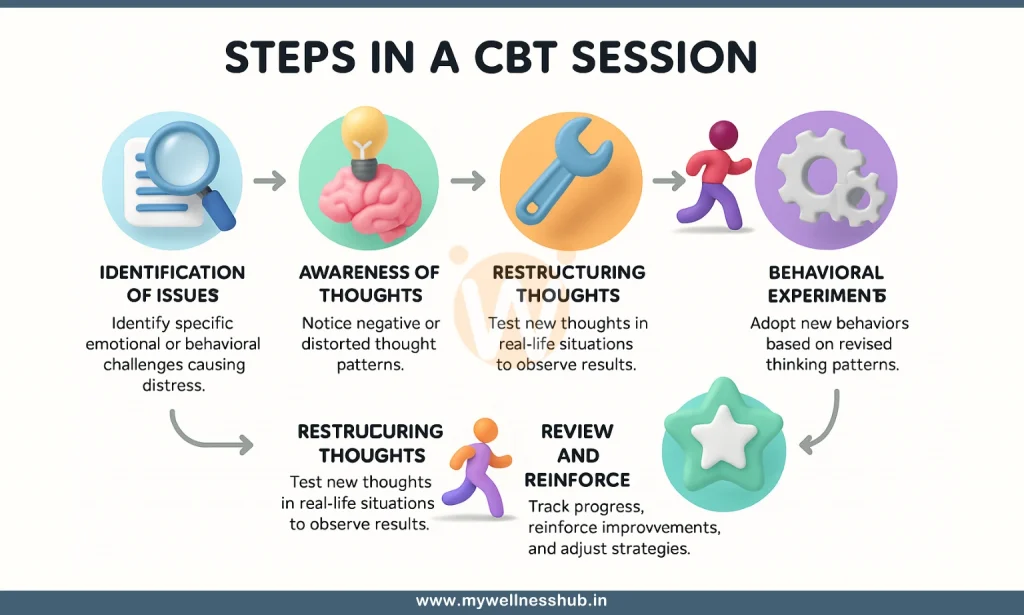
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is renowned for its structured and systematic approach to improving mental health. The process of CBT is distinctive, focusing on both the identification and modification of problematic thoughts and behaviors through a series of well-defined steps. This structured nature of CBT not only makes it unique but also contributes to its effectiveness as a short-term therapeutic strategy.
1. Identification of Troubling Conditions or Situations
The first step in a typical CBT session involves identifying specific conditions or situations in your life that cause distress. This could range from a recent breakup, challenges at work, or ongoing anxiety about social interactions. By pinpointing these specific issues, CBT helps you focus on what’s most impactful to your mental health.
2. Awareness and Restructuring of Thoughts and Beliefs
Once these situations are identified, CBT encourages a deep dive into your thoughts and beliefs about them. This is where you learn to recognize patterns of negative or inaccurate thinking that may be contributing to your emotional difficulties. For instance, you might believe that you must perform perfectly in every aspect of your life, and failing to do so makes you a failure. CBT techniques help you challenge these thoughts and reframe them into more realistic and less distressing beliefs. This step is crucial because it directly addresses the cognitive distortions that often underlie many mental health issues.
3. Modification of Behavior Patterns
With new insights into your thinking patterns, CBT then guides you to modify behaviors that reinforce your difficulties. If you tend to withdraw from friends because you feel unworthy, CBT strategies might involve gradually increasing your social interactions and observing how others respond positively, which can diminish your feelings of unworthiness.
4. Emphasizing the Goal-Oriented, Short-Term Nature of CBT
CBT is goal-oriented, with each session aimed at achieving specific objectives set by you and your therapist. This focus on specific goals helps make the therapy process clear and efficient. Typically, CBT is a short-term treatment, meaning you can see improvements in a relatively short amount of time compared to other therapies. This is particularly appealing if you’re seeking quick, practical help with issues that are clearly defined.
Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is widely recognized for its effectiveness in treating a multitude of psychological issues. It is a versatile therapy that addresses an extensive range of mental health conditions and also provides valuable tools for everyday life management, making it relevant for virtually everyone.
Treating a Range of Mental Health Conditions
CBT has proven efficacy in treating some of the most common as well as complex mental health disorders. Here are just a few:
- Depression: CBT teaches people with depression how to change negative thoughts and encourages them to take part in positive activities.
- Anxiety Disorders: CBT helps people with anxiety manage their fears by changing how they think about them, which helps reduce anxiety.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): CBT is used to help people understand and deal with their traumatic memories, which lessens the intense emotions linked to PTSD.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): CBT helps people with OCD reduce their compulsive behaviors by tackling the anxious thoughts that cause these behaviors.
- Eating Disorders: CBT addresses the harmful thinking and behaviors linked to eating disorders, helping individuals build a healthier relationship with food and their bodies.
Benefits Beyond Diagnosed Conditions
CBT isn’t just for people with mental health diagnoses; it’s also great for anyone wanting to improve their life quality. Here’s how it helps:
- Stress Management: CBT gives you tools to better handle everyday stresses from work, relationships, or other areas.
- Improving Relationships: CBT teaches you to communicate better, solve conflicts, and understand others more, making relationships more rewarding and less stressful.
- Enhancing Emotional Regulation: CBT offers techniques to manage emotions more effectively, which is useful both at home and work.
- Developing Coping Strategies: CBT helps you recognize and change negative thoughts, making it easier to deal with life’s challenges.
How Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is Conducted
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a flexible treatment that can be done in different places, which makes it easy for many people to access and benefit from it.
Different Places for CBT:
- Individual Sessions: The most common way to do CBT is in one-on-one therapy sessions with your therapist. This personalized approach lets you work closely on your issues and come up with specific ways to handle them.
- Group Therapy: CBT can also happen in groups. This lets you learn from what others are going through. It creates a community feeling and shows that you’re not alone in your struggles.
- Online Platforms: Thanks to technology, you can now do CBT online. This is great for people who have busy schedules or can’t get to a therapist’s office easily.
The Collaborative Nature of CBT
CBT is all about teamwork. In this therapy, you and your therapist team up to pinpoint problems, set goals, and see how you’re doing. This team effort makes sure the therapy meets your specific needs and gives you the tools to handle your mental health on your own.
The Role of “Homework” in CBT
CBT extends beyond the therapy sessions through the use of “homework.” These assignments might include practical exercises, journaling, or practicing new skills in real-life situations. Homework is crucial as it allows you to apply what you’ve learned in therapy to daily life, reinforcing new patterns and helping solidify the changes you are working towards.
Making the Most of CBT
No matter if you go for one-on-one sessions, join a group, or opt for online CBT, your involvement and dedication are key. Being fully engaged and doing your homework can really boost how well the therapy works, helping you manage your symptoms better in the long run.
Challenges and Considerations in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
While Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a highly effective treatment approach for various mental health issues, it is not without its challenges. Understanding these can help you set realistic expectations and make the most out of your therapy sessions.
1. Emotional Difficulties During Therapy
Engaging in CBT can sometimes be emotionally challenging. This therapy requires you to confront and change deeply ingrained patterns of thinking and behavior, which can stir up intense emotions and discomfort. For instance, addressing negative self-beliefs or confronting fears directly through exposure therapy might initially increase your anxiety or emotional discomfort.
2. Managing Challenges with Professional Guidance
In CBT, having a strong and trusting relationship with your therapist is key. They create a safe space where you can tackle tough emotions and thoughts. Your therapist is there to support you, understand you, and teach you how to cope in healthier ways.
CBT sometimes means facing the things that upset you, but your therapist will make sure this happens in a safe and controlled way. They’ll help you slowly get used to these stressors, building your ability to handle them without feeling overwhelmed.
The Importance of a Strong Therapist-Client Relationship
The effectiveness of CBT is greatly enhanced by a positive therapeutic relationship. When you trust your therapist and feel understood, you are more likely to be open and honest about your thoughts and feelings, which is crucial for the success of the therapy. Your therapist’s empathy and validation of your experiences can make it easier for you to engage in the challenging aspects of CBT and stick with the treatment even when it gets tough.
Comparing CBT to Other Therapies
| Therapy Type | Focus Area | Typical Duration | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Thoughts, behaviors, and emotions | 5-20 sessions (short-term) | Highly effective for anxiety, depression, PTSD, and other conditions; provides skills for handling future challenges |
| Psychodynamic Therapy | Unconscious processes and past experiences | Several months to years (long-term) | Effective for deep-rooted emotional issues; less structured than CBT |
| Group Therapy | Social interactions and support | Varies; often medium to long-term | Effective for building support networks, understanding social behaviors, and learning from others |
| Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) | Interpersonal relationships and social functioning | 12-16 weeks (short to medium-term) | Effective for depression and relationship conflicts; focuses on improving communication skills |
| Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) | Emotional regulation, mindfulness, distress tolerance | Typically 6 months to 1 year | Particularly effective for borderline personality disorder, chronic suicidal thoughts, and self-harm behaviors |
Finding the Right Therapist for Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Choosing the right therapist is crucial for a successful therapeutic experience, especially when engaging in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). The effectiveness of CBT greatly depends on the quality of the interaction between you and your therapist. Here are some tips to help you find the right therapist who can meet your needs effectively.
Check Qualifications and Expertise
When starting your search for a therapist, the first step is to check their qualifications and areas of expertise. It’s important that the therapist has a relevant educational background, typically a degree in psychology, counseling, or social work, and is licensed to practice in your state.
- Credentials: Look for certifications from recognized psychological associations, such as the American Psychological Association (APA) or similar bodies in your country. These credentials indicate that the therapist has met specific professional standards and adheres to a code of ethics.
- Specialization: Since CBT is a specialized form of therapy, check if the therapist has specific training and experience in CBT. Therapists with a focus on CBT will likely have a deeper understanding and more experience in applying its techniques effectively.
Assess Compatibility
The therapeutic relationship plays a significant role in the success of CBT. It’s important to find a therapist with whom you feel comfortable and can build trust.
- Consultation Session: Many therapists offer a preliminary consultation, which can be a great opportunity to assess whether their style and approach align with your needs. Use this session to discuss your goals and expectations and see if the therapist’s response resonates with you.
- Communication Style: Pay attention to how the therapist communicates. A good CBT therapist should be clear, transparent, and supportive, encouraging you to actively participate in the therapy process.
Conclusion
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is highly effective for managing various psychological issues. Its method of changing negative thoughts and behaviors has helped many people enjoy better and more balanced lives. CBT is well-supported by research, making it a trusted method for treatment.
For those looking to explore CBT and other therapy options, Wellness Hub offers a wide range of services tailored to meet your needs. We focus on providing quality care that empowers you for a healthier future. Whether you’re starting your journey to better mental health or just want to learn more, visit us at Wellness Hub. We’re here to help you overcome life’s challenges and achieve your goals.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, or CBT, is a form of psychological treatment that helps individuals manage their problems by changing negative thoughts and behaviors. It is highly effective for treating a variety of issues including anxiety, depression, and stress.
2. How does CBT differ from other forms of therapy?
Unlike other therapies that may focus extensively on discussing past events, CBT concentrates on current thoughts and behaviors. It involves working with a mental health counselor in a structured way, focusing on specific problems and learning to manage them effectively.
3. What can I expect from a CBT session?
CBT sessions are usually structured to ensure that the therapist and the client work together to identify and solve problems. The therapist helps the client learn how to change destructive or disturbing thought patterns and offers practical strategies to cope with various life challenges.
4. How long does it typically take to see results from CBT?
The duration of CBT can vary depending on the individual and their specific issues, but it is generally considered a short-term therapy. Many people see significant improvements within 5 to 20 sessions.
5. Is CBT suitable for children and teenagers?
Yes, CBT has been adapted for children and teenagers with great success. It can help young individuals manage stress, anxiety, and depression by teaching them how to process their emotions and respond to situations in healthier ways.
6. Can CBT be done online?
Absolutely! CBT is very adaptable and can be conducted online via teletherapy sessions. This makes it accessible to those who cannot attend in-person sessions due to geographic or time constraints.
7. What are the benefits of CBT?
CBT helps improve emotional regulation and develops coping strategies for dealing with different types of psychological stress. It is also effective in improving interpersonal relationships and overall mental health.
8. How do I find the right CBT therapist?
Finding the right CBT therapist involves checking their qualifications, ensuring they have specific training in CBT, and assessing whether their style and approach align with your needs. It’s also important to have a preliminary consultation to see if you feel comfortable with them.
9. What types of problems can CBT address?
CBT is versatile and can address a wide range of psychological issues, from mood disorders like depression and anxiety to behavioral problems like eating disorders and substance abuse. It is also effective in managing everyday stress and improving emotional regulation.
10. Are there different types of CBT?
Yes, there are several different forms of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, each tailored to address specific issues. Some of the most common include:
- Standard CBT, which focuses on identifying and changing negative thoughts and behaviors.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), which is particularly effective for treating personality disorders and involves concepts of mindfulness and emotional regulation.
- Cognitive Therapy, which specifically targets the thought processes that influence behaviors.
- Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), which focuses on identifying irrational beliefs and challenging these thoughts.
About Author:
Lasya Vooturi,
Clinical Psychologist (A) & Behavioral Therapist
Lasya holds a Professional Diploma in Clinical Psychology from Amity University, where she deepened her understanding of psychological principles from March 2023 to March 2024. With over a year of dedicated experience as a Behavioral Therapist, Lasya has honed her skills in applying effective therapy techniques tailored to individual needs. Fluent in Telugu, Hindi, and English, she is adept at connecting with a diverse range of clients, ensuring comprehensive communication and understanding. Lasya’s approach is grounded in empathy and scientific rigor, making her a trusted ally in navigating mental health challenges.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message








